2023年12月13日,Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism在线发表了题为“Fructose promotes liver cancer via microbial acetate-induced O-GlcNAcylation”的述评;作者为Emily M. Esquea,Riley G. Young和 Mauricio J. Reginato。
摘要:High dietary fructose consumption is linked to multiple disease states, including cancer. Zhou and colleagues recently reported a novel mechanism where high dietary fructose levels increase acetate production by the gut microbiome increasing post-translational modification O-GlcNAcylation in liver cells, which contributes to disease progression in mouse models of hepatocellular carcinoma.
关键词:果糖 肝癌 O-GlcNAc糖基化修饰 微生物 乙酸
fructose liver cancer O-GlcNAcylation microbiota acetate
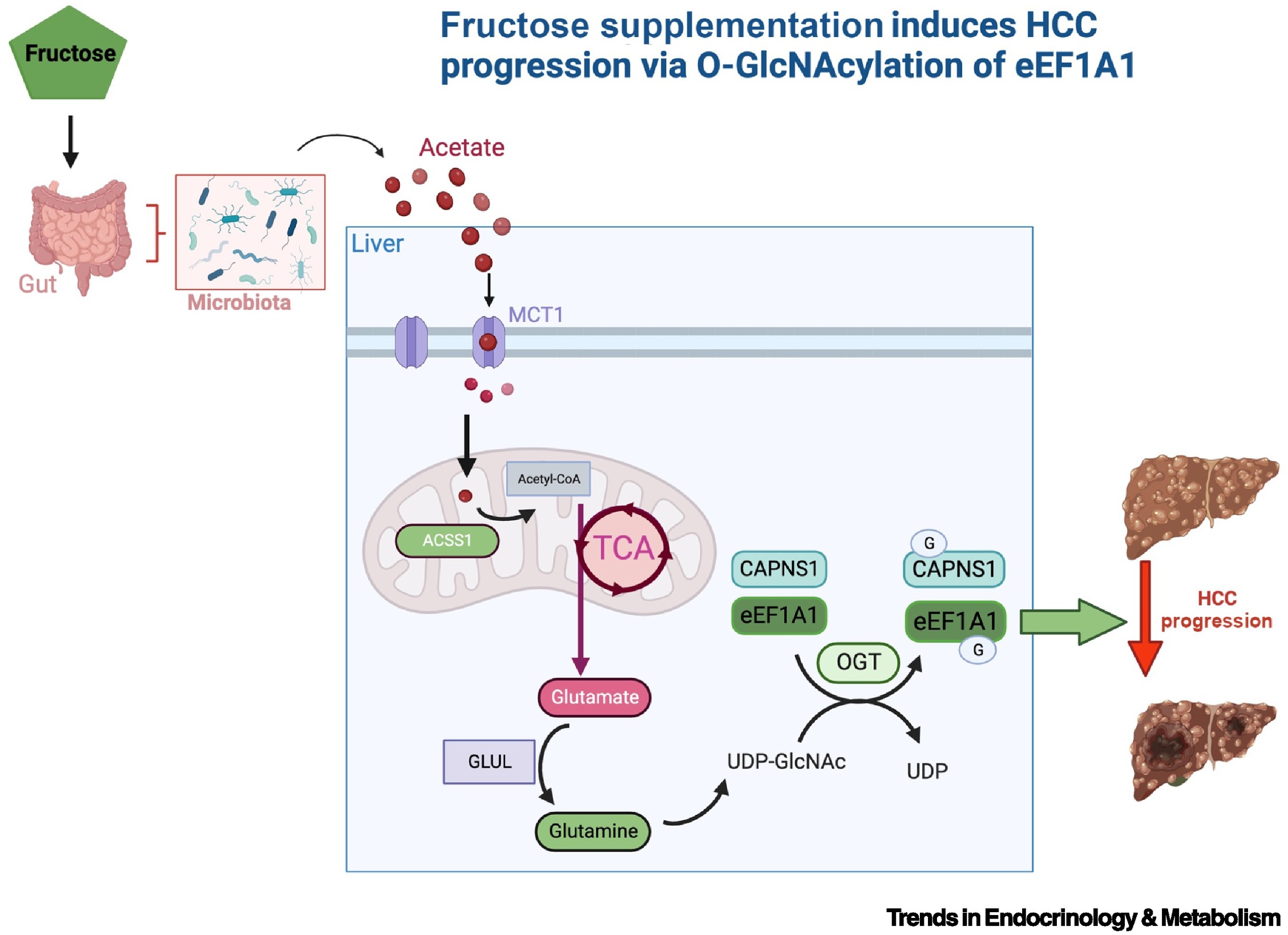
Figure 1 Fructose supplementation induces HCC progression via O-GlcNAcylation of eEf1A1 and CAPNS1.
A chemically induced (DEN/CCl4) HCC mouse model fed a high-fructose diet increased progression of liver cancer via microbiota-generated acetate, which is taken up by hepatocytes, possibly via MCT1. Acetate is converted into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria by the enzyme ACSS1; acetyl-CoA enters the TCA cycle to produce glutamate, which is converted to glutamine by GLUL. Glutamine is used to generate UDP-GlcNAc; this serves as a substrate for OGT to O-GlcNAcylate eEF1A1 and CAPNS1, which drive growth and progression of HCC. Abbreviations: ACSS1, acyl-CoA synthetase short chain family member 1; CAPNS1, calpain small subunit 1; eEF1A1, eukaryotic elongation factor 1A1; GLUL, glutamine synthase; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MCT1, monocarboxylate transporter 1; OGT, O-GlcNAc transferase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; UDP-GlcNAc, uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2023.12.002
原文链接:https://www.cell.com/trends/endocrinology-metabolism/fulltext/S1043-2760(23)00247-3