当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
J. Mater. Chem. A
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Mechanisms of oxygen transport resistance of mesoporous carbon-supported catalysts in fuel cells
Journal of Materials Chemistry A ( IF 10.7 ) Pub Date : 2024-12-11 , DOI: 10.1039/d4ta06413e
Kai-Bo An 1 , Wen-Zhen Fang 1 , Zi-Hao Xuan 1 , Guo-Rui Zhao 1 , Han Ling 1 , Wen-Quan Tao 1
Journal of Materials Chemistry A ( IF 10.7 ) Pub Date : 2024-12-11 , DOI: 10.1039/d4ta06413e
Kai-Bo An 1 , Wen-Zhen Fang 1 , Zi-Hao Xuan 1 , Guo-Rui Zhao 1 , Han Ling 1 , Wen-Quan Tao 1
Affiliation

|
Understanding the mechanisms of oxygen transport resistance of mesoporous carbon catalysts in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) is crucial to improve platinum (Pt) utilization. In this work, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were employed to unravel the origin of local oxygen transport resistance 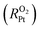 of ionomer–Pt and water–Pt catalysts on mesoporous carbons. It was found that the adsorption resistance (Rads) on Pt surfaces was dominant to
of ionomer–Pt and water–Pt catalysts on mesoporous carbons. It was found that the adsorption resistance (Rads) on Pt surfaces was dominant to 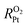 due to the formation of a dense layer. The Rads value of water–Pt catalysts was determined to be 14.32 s m−1, which was much lesser than that of ionomer–Pt catalysts. Besides, we found that Rads would be significantly affected by the presence of carbon supports, ultrathin film effects, or nearby catalysts as the carbon support would present an additional carbon dense layer, the density of which is altered when the film thickness or the distance between two Pt particles is below the threshold value. Furthermore, we calculated the oxygen transport resistance of Pt catalysts in the interior pores of mesoporous carbons, which was in good agreement with theoretical models. We found that the diffusion resistance to the local Pt nanoparticle increases nonlinearly with the depth, and the dense effect of interior Pt will lead to a remarkable increase in
due to the formation of a dense layer. The Rads value of water–Pt catalysts was determined to be 14.32 s m−1, which was much lesser than that of ionomer–Pt catalysts. Besides, we found that Rads would be significantly affected by the presence of carbon supports, ultrathin film effects, or nearby catalysts as the carbon support would present an additional carbon dense layer, the density of which is altered when the film thickness or the distance between two Pt particles is below the threshold value. Furthermore, we calculated the oxygen transport resistance of Pt catalysts in the interior pores of mesoporous carbons, which was in good agreement with theoretical models. We found that the diffusion resistance to the local Pt nanoparticle increases nonlinearly with the depth, and the dense effect of interior Pt will lead to a remarkable increase in 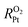 .
.
中文翻译:

燃料电池中介孔碳负载催化剂的氧输运阻力机制
了解质子交换膜燃料电池 (PEMFC) 中介孔碳催化剂的氧传输阻力机制对于提高铂 (Pt) 利用率至关重要。在这项工作中,采用分子动力学 (MD) 模拟来揭示离聚物-Pt 和水-Pt 催化剂在介孔碳上局部氧传输阻力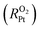 的来源。研究发现,由于形成了致密层,Pt 表面的吸附阻力 (R ads ) 占主导
的来源。研究发现,由于形成了致密层,Pt 表面的吸附阻力 (R ads ) 占主导 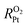 地位。水-Pt 催化剂的 R 值为 14.32 s m −1 ,远低于离聚物-Pt 催化剂的 R ads 值。此外,我们发现碳载体的存在、超薄膜效应或附近的催化剂会对 R ads 产生显着影响,因为碳载体会呈现一个额外的碳致密层,当膜厚或两个 Pt 颗粒之间的距离低于阈值时,其密度会发生变化。此外,我们计算了 Pt 催化剂在介孔碳内部孔隙中的氧传输阻力,这与理论模型吻合较好。我们发现,对局部 Pt 纳米颗粒的扩散阻力随深度非线性增加,内部 Pt 的致密效应将导致
地位。水-Pt 催化剂的 R 值为 14.32 s m −1 ,远低于离聚物-Pt 催化剂的 R ads 值。此外,我们发现碳载体的存在、超薄膜效应或附近的催化剂会对 R ads 产生显着影响,因为碳载体会呈现一个额外的碳致密层,当膜厚或两个 Pt 颗粒之间的距离低于阈值时,其密度会发生变化。此外,我们计算了 Pt 催化剂在介孔碳内部孔隙中的氧传输阻力,这与理论模型吻合较好。我们发现,对局部 Pt 纳米颗粒的扩散阻力随深度非线性增加,内部 Pt 的致密效应将导致 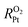 的显着增加。
的显着增加。
更新日期:2024-12-11
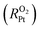 of ionomer–Pt and water–Pt catalysts on mesoporous carbons. It was found that the adsorption resistance (Rads) on Pt surfaces was dominant to
of ionomer–Pt and water–Pt catalysts on mesoporous carbons. It was found that the adsorption resistance (Rads) on Pt surfaces was dominant to 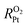 due to the formation of a dense layer. The Rads value of water–Pt catalysts was determined to be 14.32 s m−1, which was much lesser than that of ionomer–Pt catalysts. Besides, we found that Rads would be significantly affected by the presence of carbon supports, ultrathin film effects, or nearby catalysts as the carbon support would present an additional carbon dense layer, the density of which is altered when the film thickness or the distance between two Pt particles is below the threshold value. Furthermore, we calculated the oxygen transport resistance of Pt catalysts in the interior pores of mesoporous carbons, which was in good agreement with theoretical models. We found that the diffusion resistance to the local Pt nanoparticle increases nonlinearly with the depth, and the dense effect of interior Pt will lead to a remarkable increase in
due to the formation of a dense layer. The Rads value of water–Pt catalysts was determined to be 14.32 s m−1, which was much lesser than that of ionomer–Pt catalysts. Besides, we found that Rads would be significantly affected by the presence of carbon supports, ultrathin film effects, or nearby catalysts as the carbon support would present an additional carbon dense layer, the density of which is altered when the film thickness or the distance between two Pt particles is below the threshold value. Furthermore, we calculated the oxygen transport resistance of Pt catalysts in the interior pores of mesoporous carbons, which was in good agreement with theoretical models. We found that the diffusion resistance to the local Pt nanoparticle increases nonlinearly with the depth, and the dense effect of interior Pt will lead to a remarkable increase in 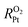 .
.
中文翻译:

燃料电池中介孔碳负载催化剂的氧输运阻力机制
了解质子交换膜燃料电池 (PEMFC) 中介孔碳催化剂的氧传输阻力机制对于提高铂 (Pt) 利用率至关重要。在这项工作中,采用分子动力学 (MD) 模拟来揭示离聚物-Pt 和水-Pt 催化剂在介孔碳上局部氧传输阻力
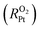 的来源。研究发现,由于形成了致密层,Pt 表面的吸附阻力 (R ads ) 占主导
的来源。研究发现,由于形成了致密层,Pt 表面的吸附阻力 (R ads ) 占主导 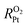 地位。水-Pt 催化剂的 R 值为 14.32 s m −1 ,远低于离聚物-Pt 催化剂的 R ads 值。此外,我们发现碳载体的存在、超薄膜效应或附近的催化剂会对 R ads 产生显着影响,因为碳载体会呈现一个额外的碳致密层,当膜厚或两个 Pt 颗粒之间的距离低于阈值时,其密度会发生变化。此外,我们计算了 Pt 催化剂在介孔碳内部孔隙中的氧传输阻力,这与理论模型吻合较好。我们发现,对局部 Pt 纳米颗粒的扩散阻力随深度非线性增加,内部 Pt 的致密效应将导致
地位。水-Pt 催化剂的 R 值为 14.32 s m −1 ,远低于离聚物-Pt 催化剂的 R ads 值。此外,我们发现碳载体的存在、超薄膜效应或附近的催化剂会对 R ads 产生显着影响,因为碳载体会呈现一个额外的碳致密层,当膜厚或两个 Pt 颗粒之间的距离低于阈值时,其密度会发生变化。此外,我们计算了 Pt 催化剂在介孔碳内部孔隙中的氧传输阻力,这与理论模型吻合较好。我们发现,对局部 Pt 纳米颗粒的扩散阻力随深度非线性增加,内部 Pt 的致密效应将导致 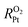 的显着增加。
的显着增加。







































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号