当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
J. Mater. Chem. A
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Efficient urea synthesis via one-step N–C–N coupling: strong metal–support interaction-driven planar Cu clusters on two-dimensional Mo2C MXene
Journal of Materials Chemistry A ( IF 10.7 ) Pub Date : 2024-06-05 , DOI: 10.1039/d4ta02393e Yue Zhang 1 , Linguo Lu 2 , Tiantian Zhao 1 , Jingxiang Zhao 1 , Qinghai Cai 1 , Zhongfang Chen 2
Journal of Materials Chemistry A ( IF 10.7 ) Pub Date : 2024-06-05 , DOI: 10.1039/d4ta02393e Yue Zhang 1 , Linguo Lu 2 , Tiantian Zhao 1 , Jingxiang Zhao 1 , Qinghai Cai 1 , Zhongfang Chen 2
Affiliation

|
The electrocatalytic co-reduction of small carbonaceous and nitrogenous molecules recently emerged as a promising strategy to mitigate carbon emissions, facilitate wastewater denitrification, and sustain urea synthesis. However, the development of highly efficient electrocatalysts to accelerate C–N coupling and multiple protonation steps remains challenging. Herein, inspired by the “strong metal–support interaction” (SMSI) concept, we designed novel catalysts, comprised of size-selected Cu clusters anchored on the two-dimensional molybdenum carbide MXene (Cun/Mo2C), for urea production via the co-reduction of nitrate (NO3−) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Our density functional theory (DFT) computations revealed that these Cu clusters are strongly immobilized on the Mo2C substrate by forming planar structures, leading to considerable active sites. Notably, these Cun/Mo2C catalysts demonstrate enhanced activity for urea synthesis through a one-step N–C–N coupling mechanism. This process involves the insertion of CO* into the 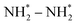 intermediate, facilitated by electrostatic attractions between their nitrogen atoms. In particular, among the catalysts tested, Cu4/Mo2C exhibits superior performance, achieving urea production with a limiting potential of −0.36 V. Furthermore, the competing side reactions, such as CO reduction or release, NH3 production, hydrogen evolution, and surface oxidation, are significantly suppressed, ensuring its high selectivity for urea synthesis. This work not only introduces a novel method for urea electro-synthesis via SMSI between metal clusters and substrate, but also suggests a strategy for synthesizing other organonitrogen compounds.
intermediate, facilitated by electrostatic attractions between their nitrogen atoms. In particular, among the catalysts tested, Cu4/Mo2C exhibits superior performance, achieving urea production with a limiting potential of −0.36 V. Furthermore, the competing side reactions, such as CO reduction or release, NH3 production, hydrogen evolution, and surface oxidation, are significantly suppressed, ensuring its high selectivity for urea synthesis. This work not only introduces a novel method for urea electro-synthesis via SMSI between metal clusters and substrate, but also suggests a strategy for synthesizing other organonitrogen compounds.
中文翻译:

通过一步N-C-N耦合高效合成尿素:二维Mo2C MXene上强金属-载体相互作用驱动的平面Cu簇
最近出现的小碳和含氮分子的电催化共还原是减少碳排放、促进废水反硝化和维持尿素合成的一种有前景的策略。然而,开发高效电催化剂来加速 C-N 耦合和多个质子化步骤仍然具有挑战性。在这里,受“强金属-载体相互作用”(SMSI)概念的启发,我们设计了新型催化剂,由锚定在二维碳化钼MXene(Cu n /Mo < b1> C),通过硝酸盐 (NO 3 − ) 和二氧化碳 (CO 2 ) 的共同还原生产尿素。我们的密度泛函理论 (DFT) 计算表明,这些 Cu 团簇通过形成平面结构牢固地固定在 Mo 2 C 基底上,从而产生大量的活性位点。值得注意的是,这些 Cu n /Mo 2 C 催化剂通过一步 N-C-N 偶联机制表现出增强的尿素合成活性。该过程涉及将 CO * 插入到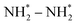 中间体中,通过氮原子之间的静电引力来促进。特别是,在测试的催化剂中,Cu 4 /Mo 2 C表现出优异的性能,以-0.36 V的极限电势实现尿素生产。此外,竞争性副反应,例如随着CO的还原或释放,NH 3 的产生、析氢和表面氧化均被显着抑制,确保了其尿素合成的高选择性。 这项工作不仅介绍了一种通过金属簇和底物之间的 SMSI 电合成尿素的新方法,而且还提出了合成其他有机氮化合物的策略。
中间体中,通过氮原子之间的静电引力来促进。特别是,在测试的催化剂中,Cu 4 /Mo 2 C表现出优异的性能,以-0.36 V的极限电势实现尿素生产。此外,竞争性副反应,例如随着CO的还原或释放,NH 3 的产生、析氢和表面氧化均被显着抑制,确保了其尿素合成的高选择性。 这项工作不仅介绍了一种通过金属簇和底物之间的 SMSI 电合成尿素的新方法,而且还提出了合成其他有机氮化合物的策略。
更新日期:2024-06-05
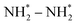 intermediate, facilitated by electrostatic attractions between their nitrogen atoms. In particular, among the catalysts tested, Cu4/Mo2C exhibits superior performance, achieving urea production with a limiting potential of −0.36 V. Furthermore, the competing side reactions, such as CO reduction or release, NH3 production, hydrogen evolution, and surface oxidation, are significantly suppressed, ensuring its high selectivity for urea synthesis. This work not only introduces a novel method for urea electro-synthesis via SMSI between metal clusters and substrate, but also suggests a strategy for synthesizing other organonitrogen compounds.
intermediate, facilitated by electrostatic attractions between their nitrogen atoms. In particular, among the catalysts tested, Cu4/Mo2C exhibits superior performance, achieving urea production with a limiting potential of −0.36 V. Furthermore, the competing side reactions, such as CO reduction or release, NH3 production, hydrogen evolution, and surface oxidation, are significantly suppressed, ensuring its high selectivity for urea synthesis. This work not only introduces a novel method for urea electro-synthesis via SMSI between metal clusters and substrate, but also suggests a strategy for synthesizing other organonitrogen compounds.
中文翻译:

通过一步N-C-N耦合高效合成尿素:二维Mo2C MXene上强金属-载体相互作用驱动的平面Cu簇
最近出现的小碳和含氮分子的电催化共还原是减少碳排放、促进废水反硝化和维持尿素合成的一种有前景的策略。然而,开发高效电催化剂来加速 C-N 耦合和多个质子化步骤仍然具有挑战性。在这里,受“强金属-载体相互作用”(SMSI)概念的启发,我们设计了新型催化剂,由锚定在二维碳化钼MXene(Cu n /Mo < b1> C),通过硝酸盐 (NO 3 − ) 和二氧化碳 (CO 2 ) 的共同还原生产尿素。我们的密度泛函理论 (DFT) 计算表明,这些 Cu 团簇通过形成平面结构牢固地固定在 Mo 2 C 基底上,从而产生大量的活性位点。值得注意的是,这些 Cu n /Mo 2 C 催化剂通过一步 N-C-N 偶联机制表现出增强的尿素合成活性。该过程涉及将 CO * 插入到
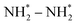 中间体中,通过氮原子之间的静电引力来促进。特别是,在测试的催化剂中,Cu 4 /Mo 2 C表现出优异的性能,以-0.36 V的极限电势实现尿素生产。此外,竞争性副反应,例如随着CO的还原或释放,NH 3 的产生、析氢和表面氧化均被显着抑制,确保了其尿素合成的高选择性。 这项工作不仅介绍了一种通过金属簇和底物之间的 SMSI 电合成尿素的新方法,而且还提出了合成其他有机氮化合物的策略。
中间体中,通过氮原子之间的静电引力来促进。特别是,在测试的催化剂中,Cu 4 /Mo 2 C表现出优异的性能,以-0.36 V的极限电势实现尿素生产。此外,竞争性副反应,例如随着CO的还原或释放,NH 3 的产生、析氢和表面氧化均被显着抑制,确保了其尿素合成的高选择性。 这项工作不仅介绍了一种通过金属簇和底物之间的 SMSI 电合成尿素的新方法,而且还提出了合成其他有机氮化合物的策略。













































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号