当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Energy Environ. Sci.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your
feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Developing post-modified Ce-MOF as a photocatalyst: a detail mechanistic insight into CO2 reduction toward selective C2 product formation
Energy & Environmental Science ( IF 32.4 ) Pub Date : 2023-03-21 , DOI: 10.1039/d2ee03755f Sanchita Karmakar 1 , Soumitra Barman 1 , Faruk Ahamed Rahimi 1 , Sandip Biswas 1 , Sukhendu Nath 2 , Tapas Kumar Maji 1
Energy & Environmental Science ( IF 32.4 ) Pub Date : 2023-03-21 , DOI: 10.1039/d2ee03755f Sanchita Karmakar 1 , Soumitra Barman 1 , Faruk Ahamed Rahimi 1 , Sandip Biswas 1 , Sukhendu Nath 2 , Tapas Kumar Maji 1
Affiliation

|
Visible light-driven C–C bond formation to produce C2-based liquid fuel selectively from CO2 is of great interest and remains a challenging task due to uphill electron transfer kinetics. Herein, we have developed [Ru(bpy)2]2+-grafted UiO-66-bpydc Ce-MOF via post-synthetic modification to harvest visible light based on MLCT (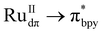 ) transition. The employment of Ru-grafted Ce-MOF facilitates fast electron transfer due to the vacant low-lying 4f orbital of CeIV, which was realized from ultrafast transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy, XANES, and in situ UV-vis spectroscopy. The synergistic effect of facile electron transfer and concomitant accommodation of two CO2 molecules in the proximal defect-site in CeIV leads to facile C–C bond formation via COOH* coupling to yield acetic acid. The catalytic assembly produces 1133 μmol g−1 of acetic acid with an impressive rate of 128 μmol g−1 h−1, suppressing the formation of other C1-based carbonaceous products in water (with selectivity 99.5%, apparent quantum yield (AQY) = 0.93%). A detailed DFT calculation has been performed to understand the mechanistic pathway of C–C bond formation, and the generation of different surface-adsorbed intermediates was further supported by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy.
) transition. The employment of Ru-grafted Ce-MOF facilitates fast electron transfer due to the vacant low-lying 4f orbital of CeIV, which was realized from ultrafast transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy, XANES, and in situ UV-vis spectroscopy. The synergistic effect of facile electron transfer and concomitant accommodation of two CO2 molecules in the proximal defect-site in CeIV leads to facile C–C bond formation via COOH* coupling to yield acetic acid. The catalytic assembly produces 1133 μmol g−1 of acetic acid with an impressive rate of 128 μmol g−1 h−1, suppressing the formation of other C1-based carbonaceous products in water (with selectivity 99.5%, apparent quantum yield (AQY) = 0.93%). A detailed DFT calculation has been performed to understand the mechanistic pathway of C–C bond formation, and the generation of different surface-adsorbed intermediates was further supported by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy.
中文翻译:

开发后改性 Ce-MOF 作为光催化剂:对 CO2 还原选择性 C2 产物形成的详细机理洞察
可见光驱动的 C-C 键形成以从 CO 2中选择性地生产 C2 基液体燃料引起了极大的兴趣,并且由于上坡电子转移动力学仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在此,我们通过合成后修饰开发了 [Ru(bpy) 2 ] 2+接枝的 UiO-66-bpydc Ce-MOF ,以基于 MLCT ( ) 跃迁获取可见光。由于 Ce IV的空置低位 4f 轨道, Ru 接枝的Ce-MOF的使用促进了快速电子转移,这是通过超快瞬态吸收 (TA) 光谱、XANES 和原位实现的 紫外-可见光谱。在 Ce IV的近端缺陷位点,两个 CO 2分子的轻松电子转移和伴随调节的协同效应导致通过COOH* 偶联轻松形成 C-C 键以产生乙酸。该催化装置产生 1133 μmol g −1的乙酸,转化率高达 128 μmol g −1 h −1,抑制了水中其他 C1 基碳质产物的形成(选择性为 99.5%,表观量子产率 (AQY)) = 0.93%)。已经进行了详细的 DFT 计算以了解 C-C 键形成的机制途径,并且进一步支持了不同表面吸附中间体的产生原位漫反射红外傅立叶变换 (DRIFT) 光谱。
紫外-可见光谱。在 Ce IV的近端缺陷位点,两个 CO 2分子的轻松电子转移和伴随调节的协同效应导致通过COOH* 偶联轻松形成 C-C 键以产生乙酸。该催化装置产生 1133 μmol g −1的乙酸,转化率高达 128 μmol g −1 h −1,抑制了水中其他 C1 基碳质产物的形成(选择性为 99.5%,表观量子产率 (AQY)) = 0.93%)。已经进行了详细的 DFT 计算以了解 C-C 键形成的机制途径,并且进一步支持了不同表面吸附中间体的产生原位漫反射红外傅立叶变换 (DRIFT) 光谱。
更新日期:2023-03-21
 ) transition. The employment of Ru-grafted Ce-MOF facilitates fast electron transfer due to the vacant low-lying 4f orbital of CeIV, which was realized from ultrafast transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy, XANES, and in situ UV-vis spectroscopy. The synergistic effect of facile electron transfer and concomitant accommodation of two CO2 molecules in the proximal defect-site in CeIV leads to facile C–C bond formation via COOH* coupling to yield acetic acid. The catalytic assembly produces 1133 μmol g−1 of acetic acid with an impressive rate of 128 μmol g−1 h−1, suppressing the formation of other C1-based carbonaceous products in water (with selectivity 99.5%, apparent quantum yield (AQY) = 0.93%). A detailed DFT calculation has been performed to understand the mechanistic pathway of C–C bond formation, and the generation of different surface-adsorbed intermediates was further supported by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy.
) transition. The employment of Ru-grafted Ce-MOF facilitates fast electron transfer due to the vacant low-lying 4f orbital of CeIV, which was realized from ultrafast transient absorption (TA) spectroscopy, XANES, and in situ UV-vis spectroscopy. The synergistic effect of facile electron transfer and concomitant accommodation of two CO2 molecules in the proximal defect-site in CeIV leads to facile C–C bond formation via COOH* coupling to yield acetic acid. The catalytic assembly produces 1133 μmol g−1 of acetic acid with an impressive rate of 128 μmol g−1 h−1, suppressing the formation of other C1-based carbonaceous products in water (with selectivity 99.5%, apparent quantum yield (AQY) = 0.93%). A detailed DFT calculation has been performed to understand the mechanistic pathway of C–C bond formation, and the generation of different surface-adsorbed intermediates was further supported by in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) spectroscopy.
中文翻译:

开发后改性 Ce-MOF 作为光催化剂:对 CO2 还原选择性 C2 产物形成的详细机理洞察
可见光驱动的 C-C 键形成以从 CO 2中选择性地生产 C2 基液体燃料引起了极大的兴趣,并且由于上坡电子转移动力学仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在此,我们通过合成后修饰开发了 [Ru(bpy) 2 ] 2+接枝的 UiO-66-bpydc Ce-MOF ,以基于 MLCT ( ) 跃迁获取可见光。由于 Ce IV的空置低位 4f 轨道, Ru 接枝的Ce-MOF的使用促进了快速电子转移,这是通过超快瞬态吸收 (TA) 光谱、XANES 和原位实现的
 紫外-可见光谱。在 Ce IV的近端缺陷位点,两个 CO 2分子的轻松电子转移和伴随调节的协同效应导致通过COOH* 偶联轻松形成 C-C 键以产生乙酸。该催化装置产生 1133 μmol g −1的乙酸,转化率高达 128 μmol g −1 h −1,抑制了水中其他 C1 基碳质产物的形成(选择性为 99.5%,表观量子产率 (AQY)) = 0.93%)。已经进行了详细的 DFT 计算以了解 C-C 键形成的机制途径,并且进一步支持了不同表面吸附中间体的产生原位漫反射红外傅立叶变换 (DRIFT) 光谱。
紫外-可见光谱。在 Ce IV的近端缺陷位点,两个 CO 2分子的轻松电子转移和伴随调节的协同效应导致通过COOH* 偶联轻松形成 C-C 键以产生乙酸。该催化装置产生 1133 μmol g −1的乙酸,转化率高达 128 μmol g −1 h −1,抑制了水中其他 C1 基碳质产物的形成(选择性为 99.5%,表观量子产率 (AQY)) = 0.93%)。已经进行了详细的 DFT 计算以了解 C-C 键形成的机制途径,并且进一步支持了不同表面吸附中间体的产生原位漫反射红外傅立叶变换 (DRIFT) 光谱。































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号