Journal of Oleo Science ( IF 1.6 ) Pub Date : 2021-09-04 , DOI: 10.5650/jos.ess21128 Kazushi Ohta 1 , Shinobu Hiraki 2 , Masakatsu Miyanabe 2 , Tatsuro Ueki 3 , Yuki Manabe 1 , Tatsuya Sugawara 1
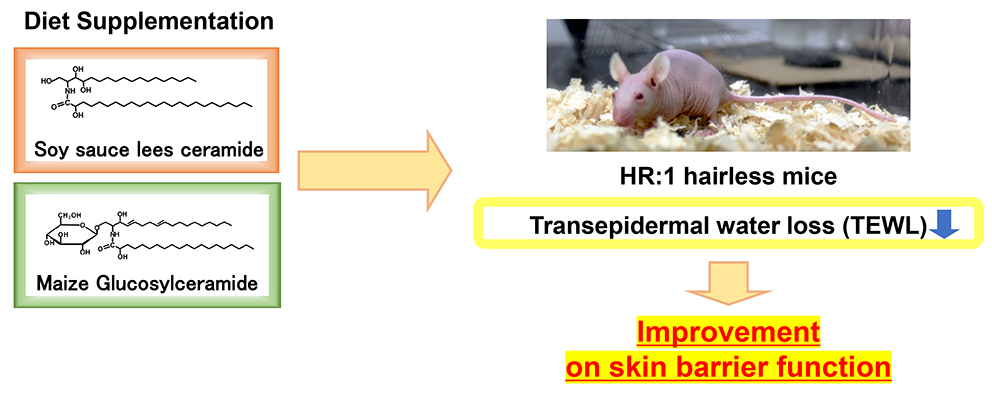
Dietary sphingolipids such as glucosylceramide and sphingomyelin are known to improve the skin barrier function of damaged skin. In this study, we focused on free-ceramide prepared from soy sauce lees, which is a byproduct of soy sauce production. The effects of dietary soy sauce lees ceramide on the skin of normal mice were evaluated and compared with those of dietary maize glucosylceramide. We found that transepidermal water loss value was significantly suppressed by dietary supplementation with soy sauce lees ceramide as effectively as or more effectively than maize glucosylceramide. Although the content of total and each subclass of ceramide in the epidermis was not significantly altered by dietary sphingolipids, that of 12 types of ceramide molecules, which were not present in dietary sources, was significantly increased upon ingestion of maize glucosylceramide and showed a tendency to increase with soy sauce lees ceramide intake. In addition, the mRNA expression of ceramide synthase 4 and involucrin in the skin was downregulated by sphingolipids. This study, for the first time, demonstrated that dietary soy sauce lees ceramide enhances skin barrier function in normal hairless mice, although further studies are needed to clarify the molecular mechanism.
 graphical abstract Fullsize Image
graphical abstract Fullsize Image
中文翻译:

用酱油酒糟制备的膳食神经酰胺可改善无毛小鼠的皮肤屏障功能
已知膳食鞘脂如葡萄糖神经酰胺和鞘磷脂可以改善受损皮肤的皮肤屏障功能。在这项研究中,我们重点关注从酱油酒糟(酱油生产的副产品)中制备的游离神经酰胺。评估膳食酱油酒糟神经酰胺对正常小鼠皮肤的影响,并与膳食玉米葡萄糖神经酰胺进行比较。我们发现,通过膳食补充酱油糟神经酰胺,可以显着抑制经表皮失水值,其效果与玉米葡萄糖神经酰胺一样有效,甚至更有效。尽管膳食鞘脂并未显着改变表皮中总神经酰胺和各亚类神经酰胺的含量,但膳食来源中不存在的 12 种神经酰胺分子的含量在摄入玉米葡萄糖神经酰胺后显着增加,并呈现出增加的趋势。增加用酱油酒糟神经酰胺的摄入量。此外,鞘脂下调皮肤中神经酰胺合酶4和外皮蛋白的mRNA表达。这项研究首次证明膳食酱油糟神经酰胺可以增强正常无毛小鼠的皮肤屏障功能,但还需要进一步研究来阐明其分子机制。

图形抽象全尺寸图像


















































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号