EuroIntervention ( IF 7.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-10-23 , DOI: 10.4244/eij-d-19-00945 Remzi Anadol 1 , Moritz Brandt , Nico Merz , Maike Knorr , Majid Ahoopai , Martin Geyer , Damian Krompiec , Philip Wenzel , Thomas Münzel , Tommaso Gori
Aims: We aimed to examine the impact of three different radiation protection devices in a real-world setting of radial artery catheterisation.
Methods and results: In an all-comer randomised trial, consecutive coronary radial diagnostic and intervention procedures were assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to shield-only protection (shield group), shield and overlapping 0.5 mm Pb panel curtain (shield+curtain group) or shield, curtain and additional 75x40 cm, 0.5 mm Pb drape placed across the waist of the patient (shield+curtain+drape group). A total of 614 radial procedures were randomised (n=193 shield, n=220 shield+curtain, n=201 shield+curtain+drape). There were no differences among the groups in patient or procedural characteristics. The primary endpoint (relative exposure ratio between the operators’ exposure in μSv and the patient’s exposure, dose area product in cGy·cm2) was significantly lower in the shield+curtain+drape group for both the first operator (20% reduction vs shield, 16% vs shield+curtain, p=0.025) and the assistant (39% reduction vs shield, 25% vs shield+curtain, p=0.009).
Conclusions: The use of an additional drape reduced the radiation exposure of both the first operator and the second operator during routine radial procedures; a shield-attached curtain alone was only partially effective. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03634657
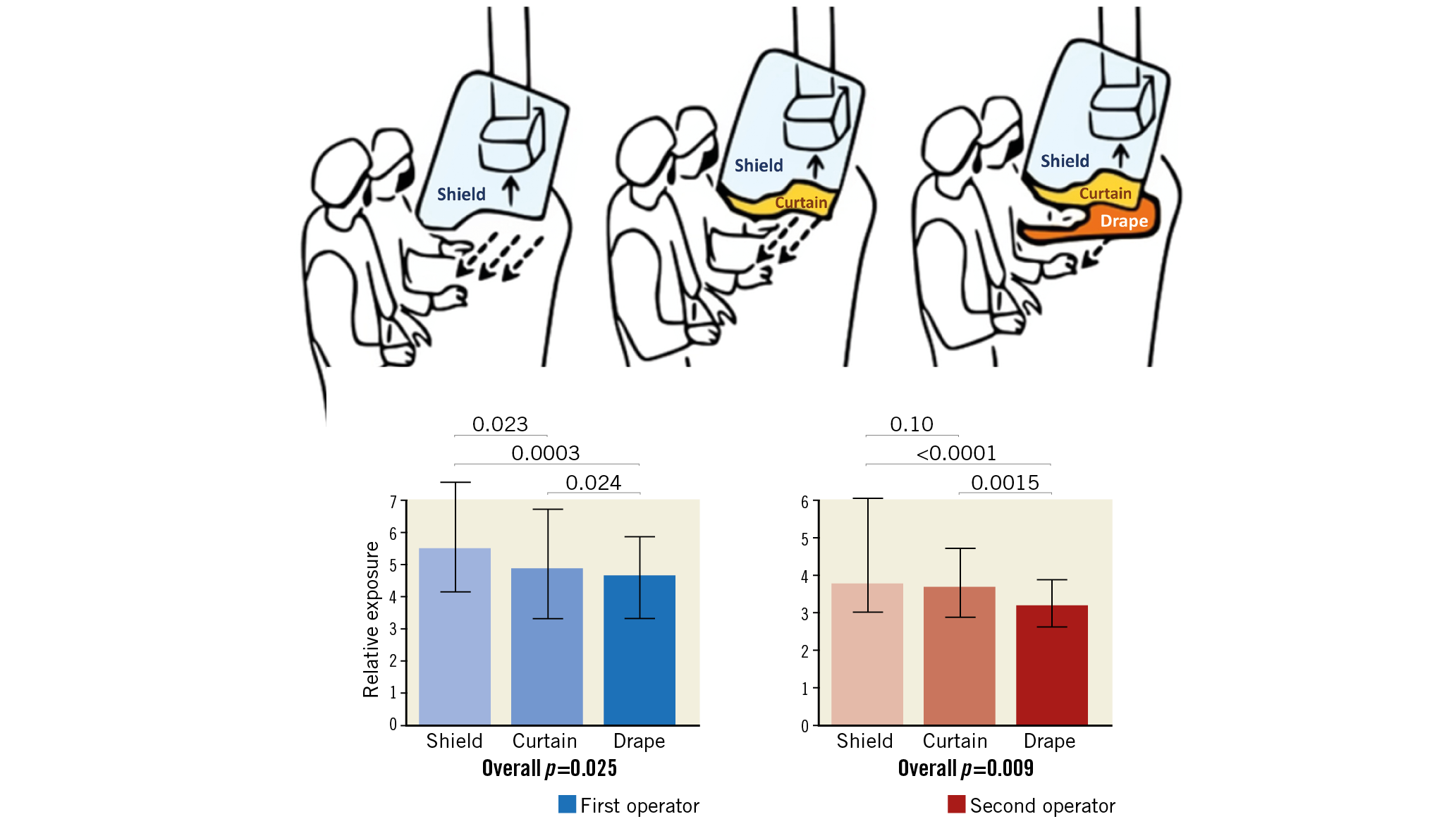
Visual summary. X-ray protection devices and their effects on radiation exposure.
中文翻译:

额外的X射线防护装置在减少径向干预中的散射辐射方面的效果:ESPRESSO随机试验。
目的:我们旨在研究在现实世界中protection动脉导管插入术中三种不同辐射防护装置的影响。
方法和结果:在一项全民随机试验中,以1:1:1:1的比例分配连续的冠状动脉radial诊和干预程序,以仅采用屏蔽(屏蔽组),屏蔽和重叠的0.5 mm Pb面板幕(屏蔽+幕布组)或屏蔽物,窗帘和另外75x40厘米,0.5毫米Pb悬垂物放置在患者的腰部(屏蔽物+窗帘+悬垂物组)。总共对614个procedures骨手术进行了随机分组(n = 193盾,n = 220盾+幕,n = 201盾+幕+悬垂)。各组患者或程序特征无差异。对于第一个操作者,防护罩+窗帘+悬垂组的主要终点(以μSv为单位的操作员暴露量与患者的暴露量之间的相对暴露率,以cGy·cm2为单位的剂量面积乘积)显着较低(相对于防护罩,减少20%, vs盾牌+窗帘为16%,p = 0。
结论:在常规骨手术期间,使用附加的盖布可以减少第一位操作者和第二位操作者的辐射暴露;单独使用带屏蔽层的窗帘仅能部分有效。ClinicalTrials.gov标识符:NCT03634657

视觉摘要。X射线防护设备及其对辐射暴露的影响。





















































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号