Nano Research ( IF 9.5 ) Pub Date : 2017-07-21 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-017-1595-2 Bingqing Wang , Wenxian Liu , Weina Zhang , Junfeng Liu
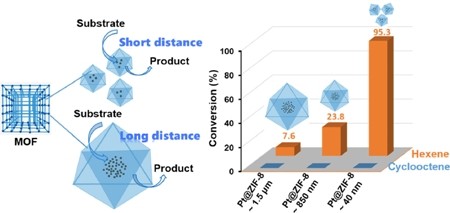
Composites incorporating nanoparticles (NPs) within metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) find applications in many different fields. In particular, using MOF layers as molecular sieves built on the NPs could enable selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis. However, such composites typically exhibit low catalytic efficiency, due to the slow diffusion of the reactants in the long and narrow channels of the MOF shell. In order to improve the catalytic efficiency of these systems, here we report the fabrication of NPs incorporated in nanosized MOFs (NPs@nano-MOFs), obtained by reducing the size of the MOF crystals grown around the NPs. The crystal size of the composites was controlled by modulating the nucleation rate of the MOFs during the encapsulation of pre-synthesized and catalytically active NPs; in this way, NPs@MOF crystals smaller than 50 nm were synthesized and subsequently used as highly efficient catalysts. Due to the shorter path from the MOF surface to the active sites, the obtained Pt@nano-MOFs composites showed a higher conversion rate than their larger-sized counterparts in the synthesis of imines via cascade reaction of nitrobenzene and in the hydrogenation of olefins, while retaining the excellent size and shape selectivity associated with the molecular sieving effect of the MOF layer. The present strategy can also be applied to prepare other encapsulated nanostructures combining various types of NPs and nano-MOFs, thus highlighting the broad potential of this approach for developing optimized catalysts with high reactivity and selectivity.
中文翻译:

纳米粒子@纳米级金属-有机骨架复合材料可作为高效的非均相催化剂,用于尺寸和形状选择反应
在金属有机框架(MOF)中结合了纳米颗粒(NPs)的复合材料在许多不同领域中都有应用。特别是,将MOF层用作构建在NP上的分子筛可以实现多相催化的选择性。然而,由于反应物在MOF壳的长而窄的通道中的缓慢扩散,这种复合材料通常表现出低催化效率。为了提高这些系统的催化效率,在这里我们报道了通过减小在NPs周围生长的MOF晶体的尺寸而获得的纳米级MOFs(NPs @ nano-MOFs)中掺入的NPs的制备。通过在预合成的具有催化活性的NP包封过程中调节MOF的成核速率,可以控制复合材料的晶体尺寸。通过这种方式,合成小于50 nm的NPs @ MOF晶体,随后将其用作高效催化剂。由于从MOF表面到活性部位的路径更短,因此在通过硝基苯的级联反应合成亚胺和烯烃的加氢反应中,所得的Pt @ nano-MOFs复合物的转化率高于其较大尺寸的复合物。同时保留与MOF层分子筛分效果相关的出色尺寸和形状选择性。本策略也可用于制备结合各种类型的NP和纳米MOF的其他封装的纳米结构,从而突出了该方法开发具有高反应性和选择性的优化催化剂的广阔潜力。由于从MOF表面到活性部位的路径更短,因此在通过硝基苯的级联反应合成亚胺和烯烃的氢化反应中,所获得的Pt @ nano-MOFs复合物的转化率高于其较大尺寸的复合物。同时保留与MOF层分子筛分效果相关的出色尺寸和形状选择性。本策略也可用于制备结合各种类型的NP和纳米MOF的其他封装的纳米结构,从而突出了该方法开发具有高反应性和选择性的优化催化剂的广阔潜力。由于从MOF表面到活性部位的路径更短,因此在通过硝基苯的级联反应合成亚胺和烯烃的氢化反应中,所获得的Pt @ nano-MOFs复合物的转化率高于其较大尺寸的复合物。同时保留与MOF层分子筛分效果相关的出色尺寸和形状选择性。本策略也可用于制备结合各种类型的NP和纳米MOF的其他封装的纳米结构,从而突出了该方法开发具有高反应性和选择性的优化催化剂的广阔潜力。在通过硝基苯的级联反应合成亚胺以及在烯烃的氢化反应中,所得的Pt @ nano-MOFs复合材料显示出比其较大尺寸的复合物更高的转化率,同时保留了与分子筛作用相关的优异的尺寸和形状选择性MOF层。本策略也可用于制备结合各种类型的NP和纳米MOF的其他封装的纳米结构,从而突出了该方法开发具有高反应性和选择性的优化催化剂的广阔潜力。在通过硝基苯的级联反应合成亚胺以及在烯烃的氢化反应中,所得的Pt @ nano-MOFs复合材料显示出比其较大尺寸的复合物更高的转化率,同时保留了与分子筛作用相关的优异的尺寸和形状选择性MOF层。本策略也可用于制备结合各种类型的NP和纳米MOF的其他封装的纳米结构,从而突出了该方法开发具有高反应性和选择性的优化催化剂的广阔潜力。
































 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号