2024年
[39] Jiguang Li, Guoyang Zhang, Grigory V. Zyryanov, Olga V. Shabunina, Xuefan Guo, Mingguang Zhu, Yulong Jin*, Zhuo Wang*. Nitric-Oxide-Enhanced Positively Charged Semiconductor Conjugated Polymer Composite Nanomaterials for Antibiofilm In Vivo. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 2415134. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Bacterial biofilms often lead to persistent infections because they provide a protective barrier and reproductive microenvironment for bacteria. Biofilms reduce the therapeutic effects of antibiotics and can easily lead to the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Therefore, development of new materials for antibiofilm with synergistic effects is crucial. In this study, positively charged near-infrared-responsive nanoparticles (TDPPB) are synthesized to control the release and delivery of nitric oxide (NO) gas. A combination of NO and photothermal therapy (PTT) is used to enhance the antibiofilm performance of TDPPB. The positive charge of TDPPB induces the nanoparticles to adhere to the surface of the bacteria. Through 808 nm laser irradiation, the local high temperature triggers the efficient release of NO from the NO donor (BNN 6) in TDPPB. TDPPB integrates the release of NO, and PTT presents good antibiofilm activity against MRSA and Escherichia coli (E. coli) biofilms. TDPPB demonstrates excellent biosafety both in vivo and in vitro, shows good antibiofilm properties in biofilm-infected mice, and promotes the healing of surface-infected sites in vivo. Because of these advantages, TDPPB can be used as a potential therapeutic agent against biofilm infections in the biomedical field.

[38] Chaofeng Zhu, Jiahao Han, Fanghui Liang, Mingguang Zhu, Guoyang Zhang, Tony D. James* and Zhuo Wang*. Advances in multi-target fluorescent probes for imaging and analyzing biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2024, 216002. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition that poses multiple challenges for disease diagnosis and treatment. Biomarker-based assays are one of the important tools for the early diagnosis of AD. In recent years, researchers have pursued the development of fluorescent probes for multi-target analysis of AD biomarkers. Herein, we review representative fluorescent probes for multi-target analysis, including analysis of Aβ and viscosity, Aβ and reactive oxygen species, various proteins (NFTs, Aβ aggregates, or Aβ oligomers), and multi-modal imaging. We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the reported probes and summarize the achievements, current challenges, and application prospects for multi-target fluorescent probes in AD.

[37] Linxing Si, Qian Wu, Yulong Jin* and Zhuo Wang*.Research progress in the detection of trace heavy metal ions in food samples. Front. Chem. 2024:1423666. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Food safety is the basis for ensuring human survival and development. The threat of heavy metal ions to food safety has become a social concern with the rapid growth of the economy and the accompanying environmental pollution. Some heavy metal ions are highly toxic even at trace levels and pose significant health risks to humans. Therefore, ultrasensitive detection of heavy metal ions in food samples is important. In this mini-review, recent advances in the analytical methods based on nanomaterials for detecting trace heavy metal ions in food samples are summarized in three categories: electrochemical, colorimetric, and fluorescent methods. We present the features and sensing mechanisms of these three methods, along with typical examples to illustrate their application in the detection of heavy metal ions in foods. This mini-review ends with a discussion of current challenges and future prospects of these approaches for sensing heavy metal ions. The review will help readers understand the principles of these methods, thereby promoting the development of new analytical methods for the detection of heavy metal ions in food samples.
[36] Guoyang Zhang, Yufan Ma, Zirui Wang, Xin Zhang, Xuefei Wang*, Sio-Long Lo*, and Zhuo Wang*. Identification of Microorganism in Infected Wounds by Positively Charged Selective Sensor Array and Deep Learning Algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 7787-7796. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Microorganism are ubiquitous and intimately connected with human health and disease management. The accurate and fast identification of pathogenic microorganisms is especially important for diagnosing infections. Herein, three tetraphenylethylene derivatives (S-TDs: TBN, TPN, and TPI) featuring different cationic groups, charge numbers, emission wavelengths, and hydrophobicities were successfully synthesized. Benefiting from distinct cell wall binding properties, S-TDs were collectively utilized to create a sensor array capable of imaging various microorganisms through their characteristic fluorescent signatures. Furthermore, the interaction mechanism between S-TDs and different microorganisms was explored by calculating the binding energy between S-TDs and cell membrane/wall constituents, including phospholipid bilayer and peptidoglycan. Using a combination of the fluorescence sensor array and a deep learning model of residual network (ResNet), readily differentiation of Gram-negative bacteria (G−), Gram-positive bacteria (G+), fungi, and their mixtures was achieved. Specifically, by extensive training of two ResNet models with large quantities of images data from 14 kinds of microorganism stained with S-TDs, identification of microorganism was achieved at high-level accuracy: over 92.8% for both Gram species and antibiotic-resistant species, with 90.35% accuracy for the detection of mixed microorganism in infected wound. This novel method provides a rapid and accurate method for microbial classification, potentially aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases.

[35] Guoyang Zhang, Zirui Wang, Lijun Ma, Jiguang Li, Jiahao Han, Mingguang Zhu, Zixuan Zhang, Shilong Zhang, Xin Zhang and Zhuo Wang*. Identification of Pancreatic Metastasis Cells and Cell Spheroids by the Organelle-Targeting Sensor Array. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2024. 2400241. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Pancreatic cancer is a highly malignant and metastatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer can lead to liver metastases, gallbladder metastases, and duodenum metastases. The identification of pancreatic cancer cells is essential for the diagnosis of metastatic cancer and exploration of carcinoma in situ. Organelles play an important role in maintaining the function of cells, the various cells show significant differences in organelle microenvironment. Herein, six probes are synthesized for targeting mitochondria, lysosomes, cell membranes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lipid droplets. The six fluorescent probes form an organelles-targeted sensor array (OT-SA) to image pancreatic metastatic cancer cells and cell spheroids. The homology of metastatic cancer cells brings the challenge for identification of these cells. The residual network (ResNet) model has been proven to automatically extract and select image features, which can figure out a subtle difference among similar samples. Hence, OT-SA is developed to identify pancreatic metastasis cells and cell spheroids in combination with ResNet analysis. The identification accuracy for the pancreatic metastasis cells (> 99%) and pancreatic metastasis cell spheroids (> 99%) in the test set is successfully achieved respectively. The organelles-targeting sensor array provides a method for the identification of pancreatic cancer metastasis in cells and cell spheroids.

[34] Peiyu Chen, Guoyang Zhang, Jiguang Li, Lijun Ma, Jiaying Zhou, Mingguang Zhu, Shuo Li* and Zhuo Wang*. Aggregation-induced Emission Probe for Fluorescence/Photoacoustic Dual-modality Imaging and Photodynamic/Photothermal Treatment. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024. 40, 293–304. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
The combination of near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging (FLI) and photoacoustic imaging (PAI) can effectively compensate for each other’s inherent limitations, which can provide reliable and rich information on tumor biology. Therefore, the development of FL/PA dual-modality imaging probes is beneficial for achieving precision cancer diagnosis and treatment. Herein, we designed an efficient phototherapy agent methoxy bithiophene indene (OTIC), which was based on aggregation-induced emission (AIE) active fluorophores. To improve the water dispersion and enrichment of OTIC at the tumor site, OTIC nanoparticles (OTIC NPs) were prepared by a nanoprecipitation method. The balance between radiation and non-radiation energy dissipation was regulated by the strong donor-acceptor interaction and intramolecular motion. So OTIC NPs exhibited bright NIR fluorescence, photoacoustic signals, efficient generation of reactive oxygen species, and high photothermal conversion efficiency under NIR irradiation. Accurate imaging of the tumor and mice sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) with OTIC NPs was visualized by NIR FL/PA dual-modal imaging. With the comprehensive imaging information provided by OTIC NPs in vivo, tumors were ablated under laser irradiation, which greatly improved the therapeutic efficacy. OTIC NPs would be possible to realize the precise guidance of FL/PA imaging for tumor treatment in the future clinical application.

2023年
[33] Jiguang Li, Guoyong Pan, Grigory V. Zyryanov, Yanghan Peng, Guoyang Zhang, Lijun Ma, Shuo Li, Peiyu Chen, and Zhuo Wang*. Positively Charged Semiconductor Conjugated Polymer Nanomaterials with Photothermal Activity for Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities In Vitro and In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2023, 15, 40864–40876. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Biofilm infections are associated with most human bacterial infections and are prone to bacterial multidrug resistance. There is an urgent need to develop an alternative approach to antibacterial and antibiofilm agents. Herein, two positively charged semiconductor conjugated polymer nanoparticles (SPPD and SPND) were prepared for additive antibacterial and antibiofilm activities with the aid of positive charge and photothermal therapy (PTT). The positive charge of SPPD and SPND was helpful in adhering to the surface of bacteria. With an 808 nm laser irradiation, the photothermal activity of SPPD and SPND could be effectively transferred to bacteria and biofilms. Under the additive effect of positive charge and PTT, the inhibition rate of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) treated with SPPD and SPND (40 μg/mL) could reach more than 99.2%, and the antibacterial activities of SPPD and SPND against S. aureus biofilms were 93.5 and 95.8%. SPPD presented better biocompatibility than SPND and exhibited good antibiofilm properties in biofilm-infected mice. Overall, this additive treatment strategy of positive charge and PTT provided an optional approach to combat biofilms.

[32] Yujie Geng, Hanchen Zhang, Guoyang Zhang, Jiaying Zhou, Mingguang Zhu, Lijun Ma, Xuefei Wang*, Tony D. James*, Zhuo Wang*. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for the In Situ Visualization of Oxidative Stress in the Brains of Neuroinflammatory and Schizophrenic Mice. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 11943–11952. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Schizophrenia is a common mental disorder with unclear mechanisms. Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation play important roles in the pathological process of schizophrenia. Superoxide anion (O2•–) is an important oxidative stress biomarker in vivo. However, due to the existence of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), few near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent probes have been used for the sensing and detection of O2•–in the brain. With this research, we developed the first near-infrared fluorescent probe (named CT–CF3) for noninvasive detection of endogenous O2•–in the brain of mice. Enabling fluorescence monitoring of the dynamic changes in O2•– flux due to the prolonged activation of microglia in neuroinflamed and schizophrenic (SZ) mice brains, thereby providing direct evidence for the relationship between oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and schizophrenia. Furthermore, we confirmed the O2•–burst in the brains of first-episode schizophrenic mice and assessed the effect of two atypical antipsychotic drugs (risperidone and olanzapine) on redox homeostasis.

[31] Lijun Ma, Yujie Geng, Guoyang Zhang, Ziwei Hu, Tony D. James*, Xuefei Wang*, Zhuo Wang*. Near-Infrared Bodipy based Molecular Rotors for β-Amyloid Imaging In Vivo. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023. 230073.(原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Aβ is one of the important biomarkers for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. Many near-infrared (NIR) probes based on the donor-π-accepter structure have been developed to detect Aβ. Most reported Aβ probes are based on the N,N-dimethylamino group as the ideal donor, which is one of the widely accepted binding units. The development of new fluorescent probes with new binding units to detect Aβ are urgently required. Therefore, we developed three anchoring molecular rotor electron donors consisting of cyclic amines of different ring sizes of, namely five-membered ring (TPyr), six-membered ring (TPip), and seven-membered ring (THAI). These new anchored molecular rotors were connected to a BODIPY and named TPyrBDP, TPipBDP, and THAIBDP. These probes exhibited high affinities (from 28 nM to 54 nM) for Aβ1-42 aggregates. The six-membered ring dye TPipBDP exhibited the highest signal-to-noise (75.5-fold) and higher affinity (28.30 ± 5.94 nM). TPipBDP can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and exhibits higher fluorescence enhancement with Tg mice than with wild-type mice.

[30] Yujie Geng, Zhuo Wang*, Jiaying Zhou, Mingguang Zhu, Jiang Liu, Tony D. James*. Recent progress in the development of fluorescent probes for imaging pathological oxidative stress. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 3873-3926.(原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Oxidative stress is closely related to the physiopathology of numerous diseases. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and reactive sulfur species (RSS) are direct participants and important biomarkers of oxidative stress. A comprehensive understanding of their changes can help us evaluate disease pathogenesis and progression and facilitate early diagnosis and drug development. In recent years, fluorescent probes have been developed for real-time monitoring of ROS, RNS and RSS levels in vitro and in vivo. In this review, conventional design strategies of fluorescent probes for ROS, RNS, and RSS detection are discussed from three aspects: fluorophores, linkers, and recognition groups. We introduce representative fluorescent probes for ROS, RNS, and RSS detection in cells, physiological/pathological processes (e.g., Inflammation, Drug Induced Organ Injury and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury etc.), and specific diseases (e.g., neurodegenerative diseases, epilepsy, depression, diabetes and cancer, etc.). We then highlight the achievements, current challenges, and prospects for fluorescent probes in the pathophysiology of oxidative stress-related diseases.

[29] Shuo Li, Guoyang Zhang, Yanghan Peng, Peiyu Chen, Jiguang Li, Xuefei Wang*, Zhuo Wang*. Tyrosinase-activated Nanocomposites for Double-modals Imaging Guided Photodynamic and Photothermal Synergistic Therapy. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 2300327.(原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Tyrosinase (TYR) is an important biomarker of melanoma. The exploration of fluorescent pr-obes-based composites is beneficial to build an integrative platform for the diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. Herein, a multifunctional nanocomposite IOBOH@BSA activated by TYR is developed for selective imaging and ablation of melanoma. The chemical structure of IOBOH enables the fluorescence (FL) imaging activated by TYR, photoacoustic (PA) imaging, and photodynamic-photothermal activity by regulating the balance between radiative decay and non-radiative decay. IOBOH combined with bovine serum albumin (IOBOH@BSA) presents the response to TYR and realizes FL imaging with mitochondria-targeting in melanoma. Moreover, IOBOH@BSA shows excellent photothermal ability and is applied for PA imaging. After IOBOH@BSA is activated by TYR, the singlet oxygen generation increases obviously. IOBOH@BSA can realize TYR-activated imaging and photodynamic-photothermal therapy of melanoma. The development of TYR-activated multifunctional nanocomposites promotes the precise imaging and improves the therapeutic effect of melanoma.

[28] Mingguang Zhu, Guoyang Zhang, Ziwei Hu, Chaofeng Zhu, Yixiang Chen, Tony D. James*, Lijun Ma*, Zhuo Wang*. A BODIPY-based probe for amyloid-β imaging in vivo. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 1903-1909. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease, and the efficient detection of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques can greatly enhance diagnosis and therapy. Most reported probes used to detect Aβ are based on the N,N-dimethylamino group. As such, the design of new Aβ-recognition units facilitates the recognition of Aβ. Herein, we present an Aβ recognition unit [4-(Boc-amino) benzene] used to develop BocBDP. BocBDP can recognize and image Aβ plaques both in vitro and in vivo through the interaction with amino acid residues Lys16 (K16), Val18 (V18), and Glu22 (E22). The hydrogen bonding interaction (1.9 Å) between the carbonyl oxygen atom in the Boc unit and the amino acid residue K16 allows BocBDP to bind strongly to Aβ, resulting in a five-fold fluorescence enhancement and a high affinity (Kd = 67.8 ± 3.18 nM). BocBDP can cross the BBB and image Aβ for at least 2 hours. We anticipate that our Aβ recognition unit will help improve the design of probes that specifically recognize Aβ.

[27] Fanghui Liang, Jian Jiang, Xinyue Yang, Guoyang Zhang, Jiaying Zhou, Jiahao Han, Yujie Geng*, Zhuo Wang*. Si-rhodamine fluorescent probe for monitoring of hypochlorous acid in the brains of mice afflicted with neuroinflammation. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 1357-1360.(原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Neuroinflammation leads to a persistent oxidative stress in the brain, and is closely related to the pathology of various neurological disorders. Hypochlorous acid (HClO) is a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that, at high levels, can cause brain tissue damage and neurogenic apoptosis. Herein, we designed and synthesized a silicon-rhodamine (SiR)-based formohydrazide (FH)-containing fluorescent probe, denoted as SiR-FH, for sensing HClO. This probe showed good selectivity, rapid response and high sensitivity. SiR-FH was successfully used to detect endogenous and exogenous HClO in living cells. Moreover, SiR-FH realized real-time monitoring of change in HClO flux in the brains of mice with LPS-induced neuroinflammation. The probe provides a practical tool for the monitoring of oxidative stress related to neuroinflammation.

[26]Jiaying Zhou, Yujie Geng, Zhuo Wang*. Fluorescent molecular probes for imaging and detection of oxidases and peroxidases in biological samples. Methods, 2023, 210, 20-35.(原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Oxidases and peroxidases are two subclasses of oxidoreductases. The abnormal expression of oxidases (such as tyrosinase, cytochrome P450 oxidases, and monoamine oxidases) and peroxidases (such as glutathione peroxidase, myeloperoxidase, and eosinophil peroxidase) is relative with some diseases. Therefore, the analysis of oxidases and peroxidases is great important for disease diagnosis and treatment. Fluorescent probes present simple protocol, high sensitivity and good stability in sensing field. Molecule fluorescent probes are constructed with chemical groups that tunes their fluorescence emission in response to binding events, chemical reactions, and the surrounding environment. A fluorescent probe is an efficient tool for visualizing the activity of enzymes in living organisms on the basis of its high specificity, sensitivity, and noninvasiveness characteristics. In this review, we focus on the sensing of oxidases and peroxidases by molecule fluorescent probes, and hope to bring new insight to wide researchers about oxidases and peroxidases in biological samples.

2022年
[25] Lijun Ma, Yajie Cai, Shuo Li, Jiguang Li, Peiyu Chen, Grigory V.Zyryanov, Dmitry S.Kopchuk, Igor S.Kovalev, ZhuoWang. New Degradable Semiconducting Polymers for Photoacoustic Imaging of λ‑Carrageenan-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model. Anal. Chem., 2022, 94, 14322-14330.(原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Semiconducting polymer has a high extinction coefficient and a long band absorption and can be used as a photoacoustic imaging contrast agent. However, nonbiodegradable semiconducting polymers may cause biosafety issues due to being retained in the body. Therefore, developing degradable semiconducting polymers is necessary for in vivo imaging. Herein, we developed three degradable semiconducting polymers with unique optical properties. We adjusted the optical properties ofsemiconducting polymers by designing the molecular structure of semiconducting polymers. Polymers with a donor−π−acceptor structure could easily improve the optical properties through adjusting the donor or acceptor units. Through adjusting the electron-donor and -acceptor units, three diketopyrrolopyrrole derivative polymers (DPPTz, DPPQu, and DPPWu) were synthesized and converted into nanosize particles. By introducing the degradable chemical groups in the main chain structure of semiconducting polymers, diketopyrrolopyrrole polymers could be degraded by ClO−. Among these nanosize particles, DPPTz and DPPQu NPs were used to achieve the in vivo photoacoustic imaging of λ-carrageenan-induced arthritis mouse model. This work provides a novel design idea for the designing of red-shifted semiconducting polymer with degradable properties

[24] Xinhui Hou , Shuo Li , Zhenguo Wang , Guoyang Zhang , Zhuo Wang*. Antifungal CoAl layered double hydroxide ultrathin nanosheets loaded with oregano essential oil for cereal preservation. Food Chemistry 397 (2022) 133809. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Fungal infestation of cereals seriously affects human health and the economy. Protecting cereals from fungal infestation is meaningful. Therefore, safe and economical antifungal agents must be explored. Oregano essential oil (OEO) has broad-spectrum antifungal activity but is unstable and poorly water-dispersible. CoAl-LDH ultrathin nanosheets (CoAl-LDH UNs) are a biosafe carrier with peroxidase-like activity and good water dispersibility. A new nanocomposite was constructed by integrating OEO and CoAl-LDH UNs named OEO/CoAlLDH UNs. The antifungal activity of OEO was improved for the synergetic effect of OEO and CoAl-LDH UNs. OEO/CoAl-LDH UNs showed excellent antifungal activity against Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium graminearum and Aspergillus flavus. A polyvinyl alcohol film containing OEO/CoAl-LDH UNs was prepared as a food package and effectively inhibited fungal infestation on cereals. This work can provide some insights for the exploration of other new antifungal materials. The good biosafety of this antifungal material can be effectively applied to food packaging.

[23] Shuo Li, Yuzhi Chen, Peinan He, Yufan Ma, Yajie Cai, Xinhui Hou, Guoyang Zhang, Xin Zhang,* Zhuo Wang.*Aggregation-induced Emission (AIE) Photosensitizer Combined Polydopamine Nanomaterials for organelle-targeted Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy by the Recognition of Sialic Acid. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2022. (原文连接)
ABSTRACT
The construction of organelle-targeted nanomaterials is an effective way to improve tumor imaging and treatment. Here, we have developed a new type of composite nanomaterial named as PTTPB. PTTPB is composed of organelle-targeted aggregation-induced emission (AIE) photosensitizer TTPB and polydopamine nanomaterials (PDA). With the functional modification of TTPB, PTTPB can recognize sialic acid (SA) on the cell membrane and present mitochondrial targeted capabilities. The intake of PTTPB in cancerous cells could be increased by the recognition process of cell membrane. PTTPB can generate singlet oxygen for photodynamic therapy (PDT), and present good photothermal conversion ability with irradiation. The PTTPB with organelle targeted -guided can realize the tumor ablation with the synergetic effect of PDT & PTT.

[22] Shuo Li, XinHui Hou, Yufan Ma, Zhuo Wang*. Phenylboronic acid-based functional chemical materials for fluorescence imaging and tumor therapy. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3, 2520–2532. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Various functional chemical materials have been widely used in imaging and tumor therapy. Targeted ligands such as antibodies, peptides, and small molecules have been combined with functional materials to enhance cellular uptake, which are used for active targeting of cancer cells and tumors. Among them, phenylboronic acid (PBA), as a small molecular ligand, has the characteristics of low cytotoxicity and being modified easily. PBA improves the cancer cell imaging and tumor treatment effect by binding to glycans on the surface of cancer cells. In the minireview, we introduced the modification strategy and targeting strategy of PBA. We focused on the applications of PBA-based functional materials in fluorescence imaging and tumor therapy. For fluorescence imaging, it proved the potential of PBA-based functional chemical materials in cancer diagnosis and tumor targeting by cell imaging and in vivo imaging. For tumor therapy, we mainly discussed the applications of PBA based functional chemical materials in chemotherapy, gene therapy, phototherapy and immunotherapy. PBA-based functional chemical materials provide a useful method for cancer diagnosis and treatment.

[21] Yujie Geng, Guoyang Zhang, Yuzhi Chen, Yanghan Peng, Xuefei Wang*, Zhuo Wang*. The Si-Rhodamine Derivatives for Brain Fluorescence Imaging and monitor of H2S in the brain of Schizophrenic Mice Before and After treatment. Anal. Chem. 2022. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Schizophrenia is a common type of serious mental illness with an unclear etiology. Recently, the excessive production of hydrogen sulfide in the brain has been considered to be one of the pathophysiological bases of schizophrenia. However, due to the existence of the blood−brain barrier (BBB), almost no fluorescent probe has been successfully used for the sensing and detection of H2S in the brain. Herein, we designed and synthesized a series of near-infrared fluorescent probes SiR-Bs based on a hemicyanine and Si-rhodamine structure. Among them, Mindo-SiR presented a good penetration ability of the BBB, a high brain uptake (transport: 4.95% ID/g at 5 min), and good response to H2S in vitro and in vivo. For the first time, a fluorescent probe was used to image the changes of H2S in the brains of schizophrenic (SZ) mouse models, and it was successfully proven that there was an abnormally high level of H2S in the brains of SZ mice. Moreover, the therapeutic effect of risperidone for the treatment of SZ could be evaluated by the changes of SiR-Bs’ fluorescence imaging.

2021年
[20] Jiang Liu, Lijun Ma, Guoyang Zhang, Yuzhi Chen*, Zhuo Wang*. Recent Progress of Surface Modified Nanomaterials for Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species in Organism. Bioconjugate chem. 2021, 32, 11, 2269–2289. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential for normal physiological processes and play important roles in signal transduction, immunity, and tissue homeostasis. However, excess ROS may have a negative effect on the normal cells leading to various diseases. Nanomaterials are an attractive therapeutic alternative of antioxidants and possess an intrinsic ability to scavenge ROS. Surface modification for nanomaterials is a critical strategy to improve their comprehensive performances. Herein, we review the different surface modified strategies for nanomaterials to scavenge ROS and their inherent antioxidant capability, mechanisms of action, and biological applications. At last, the primary challenges and future perspectives in this emerging research frontier have also been highlighted. It is believed that this review paper will offer a top understanding and guidance on engineering future high-performance surface modified ROS scavenging nanomaterials for wide biomedical applications.

[19] Lijun Ma, Shu Yang, Yufan Ma, Yuzhi Chen, Zhenguo Wang, Tony D. James,* Xuefei Wang,* Zhuo Wang.* Benzothiazolium Derivatives Capped Silica Nanocompites for βamyloid Imaging in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 37, 12617–12627. (原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease, and β-amyloid (Aβ) is believed to be a causative factor in AD pathology. The abnormal deposition of Aβ is believed to be responsible for progression of AD. In order to facilitate the imaging of Aβ in vivo, suitable probe molecules with a near-infrared emission wavelength that can penetrate the blood–brain barrier (BBB) were utilized. The commercial fluorescent probe thioflavin-T (ThT) is used to image Aβ; however, because of its short emission wavelength and poor BBB penetration, ThT can only be used in vitro. With this research, based on ThT, we design three fluorescent probes (SZIs) having a longer emission wavelength in order to image Aβ aggregates. SZIs with different numbers of double bonds respond to Aβ aggregates. The SZIs have a structure similar to ThT, and as such, the SZIs are also unable to penetrate the BBB. To deal with the problem, we develop nanocomposites (MSN-Lf@SZIs) to deliver SZIs into the brain of AD mouse and image Aβ successfully. These new nanocomposites are able to deliver the dyes into the brain and facilitate Aβ imaging in vivo.

2020年
[18] Yuanyuan Zhang, Yufan Ma, Zhuo Wang*, Xueyan Zhang, Xin Chen, Shicong Hou * and Hongmei Wang *. A novel colorimetric and far-red emission ratiometric fluorescent probe for the highly selective and ultrafast detection of hypochlorite in water and its application in bioimaging. Analyst, 2020, 145, 939 (原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl)/hypochlorite (OCl−), an important reactive oxygen species, plays a number of important roles in various physiological processes. However, abnormal levels of OCl− can cause many serious diseases, such as atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. The development of efficient methods to monitor OCl− in biological systems is therefore of particular importance. Thus, we herein report a novel isophorone-based fluorescent probe, i.e., DCOH-FR-OCl, for OCl− detection. This probe was found to exhibit colorimetric and far-red ratiometric fluorescence response signals, excellent selectivity and sensitivity for OCl− (detection limit, 88.06 nM), a remarkably large Stokes shift (158 nm), an ultrafast response (completed within 3 s), perfect photostability, and good water solubility (100% in aqueous media). DCOH-FR-OCl, as we know, is the first probe that can detect OCl− by using two different response signals at an ultrafast speed with a large Stokes shift in fully aqueous media. Furthermore, DCOH-FR-OCl can be successfully employed in the real-time imaging of endogenous and exogenous OCl− in living cells.

[17] Pan Guoyong, Li Yawen1, Ma Lijun1, Ma Yufan1, Ai Wenting1, Wang Zhenguo1, Hou Xinhui1, Grigory V·Zyryanov, Wang Zhuo. New Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Agent by the Synergetic Effect of Positive Charge and Photothermal Conversion. Chemical journal of Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4):670-681.
ABSTRACT
Because of the abuse of antibiotics and the emergence of bacterial resistance, the new antibacterial agents are required urgently. Herein, we prepared semiconducting polymer nanoparticles(SP-PPh3 NPs) with synergistic antibacterial activity due to photothermal properties and positive charge. SP-PPh3 NPs have broad-spectrum antibacterial properties against Gram-negative Escherichia coli(E. coli) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus(S. aureus). The photothermal conversion efficiency of SP-PPh3 NPs is 43.8%. Moreover, the positive charge of SP-PPh3 NPs can adhere to bacteria, which is helpful to transmit heat to bacteria effectively. Under the synergistic effect of heat and positive charge, the antibacterial rates of E. coli and S. aureustreated with SP-PPh3 NPs are 99.9% and 98.6% in vitro, respectively. In addition, SP-PPh3 NPs have good biocompatibility and have almost no side effects on the major organs of mice. The bacteria-infected skin wounds on mice can completely heal after 12 d treated with SP-PPh3 NPs.

[16] Ruohao Zhang, Jie Yu, Kun Ma, Yufan Ma*, and Zhuo Wang*. Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Antibacterial Effects of Polyelectrolyte-Functionalized Gold Nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
With the increasing threat of bacterial infection to human health, the development of different antimicrobial agents is essential. Therefore, based on the photothermal conversion properties of gold nanomaterials, the polyelectrolyte (PE)-coated gold nanorods (GNR@PE) and gold nanostars (GNS@PE) are designed and synthesized. Consequently, the chemo-photothermal synergistic antibacterial effect is achieved. GNR@PE effectively eliminates the high toxicity of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and both GNR@PE and GNS@PE have good biocompatibility and stability. Because of the cation coating, GNR@PE and GNS@PE show high localized surface charge, which causes strong affinity to bacteria and destruction of bacterial cell walls and cell membranes. They have good chemical antibacterial effects, and the chemical antibacterial rates are above 50%. Under the irradiation of an 808 nm laser, for Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria, GNR@PE (50.00 μg/mL) and GNS@PE (55.00 μg/mL) can kill more than 99% of bacteria through chemo-photothermal effects. GNR@PE and GNS@PE can help eliminate inflammation caused by infection and promote wound healing in the mice model and have few side effects on the organs of mice.

[15] Xin Chen, Yufan Ma, Yuanyuan Zhang, Qing Chen, Hongmei Wang, Zhuo Wang*. A Selective and Reversible Fluorescent Probe for Zn2+ Detection in Living Cells. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
A newly 8‐aminoquioline based fluorescent probe (NQA) was designed and synthesized as a good turn‐on fluorescence sensor to reversibly detect Zn2+. The probe can detect Zn2+ in an aqueous solution with good selectivity without interference from other metal ions (Cd2+ in particular). And the limit of detection was calculated to be 2.15×10−9 M. The probe can efficiently monitor the change of concentration of Zn2+ in a broad pH range from 4.0 to 11.0. NQA can detection of Zn2+ reversibly based on the coordination interaction. NQA is biocompatibility and can be used to monitor the concentration of Zn2+ in living cells without the interference from other similar cations, especially Cd2+.

[14] Wenting Ai, Zhiqiang Yang, Yufan Ma, Xiaomin Han, Yuzhi Chen, Kui Zhu* and Zhuo Wang *. Combined tetraphenylethylene fluorogens with positive charge for imaging capsule-covered pathogens. Analyst, 2020,145, 6435-6440.(原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Capsule-covered pathogens can cause serious infectious diseases, and are highly pathogenic to humans. Herein, we developed four positively charged tetraphenylethylene derivatives (PC-TPEgens) that in certain combinations were applied to identify capsule-bearing pathogens using fluorescence imaging. The dual-charged probes were used to visualize the entire process of phagocytosis of pathogens into macrophages.

[13] Yufan Ma, Wenting Ai, Jia Huang, Lijun Ma, Yujie Geng, Xiaolei Liu, Xuefei Wang*, Zhiying Yang*, and Zhuo Wang*. Mitochondria-Targeted Sensor Array with Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens for Identification of Various Cells. Anal. Chem. 2020. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Accurate discrimination of cancerous cells is a good solution for early diagnosis of tumors. The mitochondrion plays an important role in cells. Herein, the five aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) with various double positive charges are synthesized to image mitochondria. Tetraphenylethylene (TPE) molecules are modified by methoxy groups, conjugated donor–acceptor, and different positive charges to achieve multicolor emission. The five AIEgens form the PTx-Sa (positive mitochondria-target molecular sensor array) to perform cross-fluorescence response based on the mitochondria-targeted imaging to achieve the discrimination of various cells. Principal component analysis of the cross-response fluorescence data of PTx-Sa shows that 100% accurate identification of various cells, including cancer cells and normal cells, digestive tract cancer cells, gastric cancer cells, and mixed gastric cancer cells. By support vector machine to show the predictive ability of PTx-Sa to unknown cells by using blind samples. This is the first time to apply mitochondria-targeted sensor array to identification of various cells.

[12] Xiaomin Han,Yufan Ma,Yuzhi Chen,Xuefei Wang, Zhuo Wang.Hydrogen Bond Enhanced the Aggregation-induced Emission for Visualizing Hypochlorous Acid in Inflammation Model and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model. Anal. Chem. 2020. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
As an important reactive oxygen species, hypochlorous acid (HClO) is produced in various physiological processes. The ab-normal rise of HClO level is associated with a large number of inflammatory diseases. In this work, we develop a simple aqueous soluble AIE probe for sensing HClO with significant aggregation-induced fluorescence. (>1000 times) Two probes CH3O-TPE-Py+-N+ (COTN) and OH-TPE-Py+-N+ (HOTN) are synthesized for sensing HClO by the cleavage of Py+-N+ group. The reaction products are CH3O-TPE-CHO (COT) and OH-TPE-CHO (HOT) separately. The hydrophobicity of the probes is changed with the increased aggregation-induced emission. During the process, HOTN shows greatly better response than COTN. The slight different chemical structure of COTN and HOTN results the significant response to HClO. The theoretical calculation data support that the hydrogen bond is contributed to the excellent sensitivity for HClO. On the basis of the good response to HClO in vitro, HOTN is used to imaging inflammation and hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo, because these dis-eases always are accompanying with high HClO level.

2019年
[11] Yufan Ma, Huiping Wang, Shan Su, Yuzhi Chen, Yawen Li, Xuefei Wang and Zhuo Wang , A red mitochondria-targeted AIEgen for visualizing H2S in living cells and tumours, Analyst, 2019,144, 3381-3385. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) exists in the cytosol and mitochondria of mammalian cells as a signaling molecule. Scientists have explored many important physiological functions of H2S, such as regulating vasodilator relaxation, protecting living cells and avoiding damage. The measurement of H2S is therefore necessary for exploring the biological function of cells and tissues. Herein, we report the design and synthesis of a new aggregation-induced emission luminogen (AIEgen) with greater conjugation and more positive charges, based on previous research on mitochondrial-targeted luminogens. The Indo-TPE-Indo can enter cells rapidly, as compared with an AIEgen with only one indolium (TPE-indo), and can selectively recognize HS− in mitochondria with the nucleophilic reaction of indolium and HS−. The linear range (1–100 μM) of HS− sensing can satisfy the requirement for HS− concentration in living cells and tumors.

[10] Kun Ma, Yawen Li, Zhenguo Wang, Yuzhi Chen, Xin Zhang, Chunyuan Chen, Hao Yu, Jia Huang, Zhiying Yang, Xuefei Wang, and Zhuo Wang, Core−Shell Gold Nanorod@Layered Double Hydroxide Nanomaterial with Highly Efficient Photothermal Conversion and Its Application in Antibacterial and Tumor Therap, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019. (原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Photothermal conversion efficiency (η) of gold nanorods (GNRs) can be tuned by enlarging the aspect ratio and forming the core–shell structure. Herein, an easy synthesis method is developed to construct the core–shell GNR@LDH nanostructure with GNRs and layered double hydroxides (LDHs). The interaction between Au and LDHs results some electron deficiency on the surface of Au and the more electrons induce more thermal energy conversion. The η value of GNR@LDH can reach up to 60% under the 808 nm laser irradiation, which is a significant enhanced conversion efficiency compared with the reported GNR-based photothermal therapy materials. CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) can be replaced totally during the synthesis process, and GNRs maintain a good dispersion in LDHs. This core–shell composite GNR@LDH can be applied in photothermal, antibacterial, tumor therapy and biological imaging with low dosage and nontoxicity.

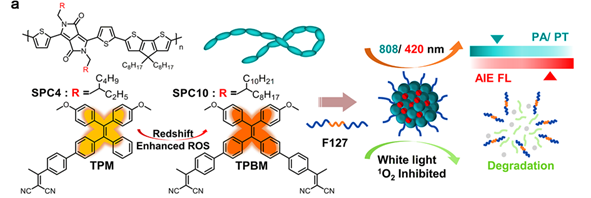
[9] Yawen Li Zitong Liu Yufan Ma Yuzhi Chen Kun Ma Xuefei Wang Deqing Zhang Zhuo Wang. Semiconducting Nanocomposite with AIEgen‐Triggered Enhanced Photoluminescence and Photodegradation for Dual‐Modality Tumor Imaging and Therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019. (原文链接)
ABCTRACT
Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles (SPNs) have potential in biological applications. While some SPNs have significant photothermal conversion efficiencies (PCEs) as photothermal and photoacoustic agents, other SPNs offer high fluorescence yields as photoluminescent agents. However, the energy balance distribution in SPNs inhibits their successful applications in photoluminescence/photoacoustic (PL/PA) dual‐modality imaging. Additionally, the ultrastability of SPNs in vivo may cause damage to organisms. This work reports nanocomposite semiconducting polymer and tetraphenylethene nanoparticles (STNPs) constructed by semiconducting polymers (SPs) and tetraphenylethene aggregation‐induced emission luminogens (TPE AIEgens). The SP SPC10 endows good photothermal conversion ability, and the AIEgen TPBM supports enhanced photoluminescence of the STNPs. The results show that the STNPs can act as PL/PA dual‐modality imaging agents. The signal‐to‐noise (S/N) ratio in the PL modality reaches 8.7, and the imaging depth in the PA modality is 5.8 mm. The SPC10 in the STNPs can be decomposed under 90 mW cm−2 white light irradiation in 6 h without any other additional agents. Furthermore, the STNPs are sufficient for the treatment of xenograft 4T1 tumor‐bearing mice based on photothermal therapy. The nanocomposite STNPs achieve optimized dual‐modality PL/PA imaging and the AIEgen‐triggered in situ photodegradation of SPNs. These properties indicate the significant potential of STNPs in clinical diagnosis and noninvasive therapy.
2018年
[8] Yuzhi Chen, Wenting Ai, Xuan Guo, Yawen Li, Yufan Ma, Lifang Chen, Hui Zhang, Tongxin Wang,* Xin Zhang,* and Zhuo Wang*. Mitochondria-Targeted Polydopamine Nanocomposite with AIE Photosensitizer for Image-Guided Photodynamic and Photothermal Tumor Ablation. Small, 2018. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT) are two kinds of treatment for tumors. Herein, a new aggregation-induced emission (AIE)gen (MeO-TPE-indo, MTi) is synthesized with a D– π –A conjugated structure. MTi, which has an electron donor and an acceptor on a tetraphenylethene (TPE) conjugated skeleton, can induce the effective generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) for PDT. With the guide of the indolium group, MTi can target and image mitochondrion selectively. In order to get good dispersion in water and long-time retention in tumors, MTi is modified on the surface of polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA NPs) to form the nanocomposite (PDA-MeO-TPEindo, PMTi) by π – π and hydrogen interactions. PMTi is a nanoscale composite for imaging-guided PDT and PTT in tumor treatment, which is constructed with AIEgens and PDA for the first time. The organic functional molecules are combined with nanomaterials for building a multifunctional diagnosis and treatment platform by utilizing the advantages of both sides.

[7] Li, Yawen,Chen, Yuzhi,Yu, Hao,Tian, Limei,Wang, Zhuo. Portable and Smart Devices for Monitoring Heavy Metal Ions Integrated with Nanomaterials. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2017:S0165993617303254. (原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
With increasing concerns of ecological environment, safe drinkable water and healthy food, the detection for heavy metal ions (HMIs) becomes an attractive research field. On the basis of optical, electrical and other signals from nanomaterials, many interesting methods and portable devices for detection of HMIs are growing flourishingly. In this review, we focus on the portable and smart devices integrated with nanomaterials for monitoring HMIs. The interesting design of the miniaturization, portability, and commercialization of HMIs detection devices are summarized and introduced comprehensively.

[6] YehuiWu, YuzhiChen, YawenLi, JiaHuang, HaoYu, ZhuoWang. Accelerating peroxidase-like activity of gold nanozymes using purine derivatives and its application for monitoring of occult blood in urine[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 270:443-451. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) is an important kind of nanozymes and a variety of its artificial enzymatic activities have been reported, such as oxidase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase. The DNA with poly purine-modified AuNPs shows an enhancement peroxidase activity compared with poly pyrimidine-modified AuNPs. In this work, purine derivatives are modified on the surface of AuNPs. The peroxidase-like activity of AuNPs is dependent on the chemical structure of the molecules capped on the surface. We find that ferric ions can accelerate the mimic enzymatic ability of 2, 6-diaminopurine (DAP) modified AuNPs. The enhanced catalytic activity comes from the synergistic reaction of AuNPs and ferric ions. The cooperative system can be applied to measure hemoglobin and red blood cells in urine with better sensitivity. Generally, there is no or few red blood cells in human urine. The presence of blood in the urine is closely related with serious diseases, for example chronic nephrotic syndrome and urinary system tumors. Compared the commercial urine test paper, the method based on DAP-AuNPs has a good sensitivity and wider quantitative range and will be helpful to do urine test at home.

[5] Zhuo Wang*, Hao Yu, Kun Ma, Yuzhi Chen, Xiuquan Zhang, Tongxin Wang, Sanbao Li, Xiaoqun Zhu, and Xuefei Wang*. Flower-like Surface of Three-Metal-Component Layered Double Hydroxide Composites for Improved Antibacterial Activity of Lysozyme. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2018:acs.bioconjchem.8b00305-.(原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Microbes play an important function in our lives, while some pathogenic bacteria are responsible for many infectious diseases, food safety, and ecological pollution. Layered double hydroxide (LDH) is a kind of natural two-dimensional material and has been applied in many fields. Lysozyme is a green natural antibacterial agent, while the antimicrobial activity of lysozyme is not as good as antibiotics. We use a different ratio of cations to tune the morphology of LDH covered with lysozyme to enhance the antibacterial ability of lysozyme. We synthesize MgAl-LDH, ZnAl-LDH, and ZnMgAl-LDH covered with lysozyme, characterize the structure and morphology, test the antibacterial in culture media, and evaluate the biotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. The flower-like structure of ZnMgAl-LDH has a rough surface, covered with lysozyme with a perfect ring, and presents good antibaterial properties and promotes wound healing of mice. The bloom flower structure of ZnMgAl-LDH can enhance the loading rate of lysozyme; meanwhile, the rougher surface can adhere more bacteria, so lyso@ZnMgAl-LDH presents better antibacterial activity than the binary LDHs.

[4] Zhuo Wang*, Yuzhi Chen, Hui Zhang, Yawen Li, Yufan Ma, Jia Huang, Xiaolei Liu, Fang Liu, Tongxin Wang, and Xin Zhang. Mitochondria-targeting Polydopamine Nanocomposites as Chemo-photothermal Therapeutics for Cancer. Bioconjugate Chemistry, 2018:acs.bioconjchem.8b00325-. (原文链接 )
ABSTRACT
Mitochondria play a key role in a variety of physiological processes, and mitochondria-targeting drug delivery is helpful and effective in cancer therapy. Rhodamine123 (Rhod123) and Doxorubicin (Dox) are not new chemical molecules, and they both can inhibit the growth of cancerous cells. Here, we combine these two “old” chemicals with polydopamine nanoparticles (PDA NPs) to strengthen the antitumor effect with the aid of near-infrared irradiation. PDA NPs carry these two chemicals tightly by hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking besides chemical bonds. The better antitumor profile of PDA-Rhod-Dox comes from the mitochondria-targeting delivery, which decreases ATP in living cells, causing apoptosis of cancerous cells effectively and inhibiting the growth of tumors in mice. The synergistic effect of PDA, Rhod123, and Dox improves the treatment effect of conventional chemotherapy drugs.

[3] Yufan Ma, Yawen Li, Kun Ma, Zhuo Wang. Optical colorimetric sensor arrays for chemical and biological analysis[J]. Science China(Chemistry), 2018, v.61(06):15-27. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
In recent years, the sensor array has attracted much attention in the field of complex system analysis on the basis of its good selectivity and easy operation. Many optical colorimetric sensor arrays are designed to analyze multi-target analytes due to the good sensitivity of optical signal. In this review, we introduce the targeting analytes, sensing mechanisms and data processing methods of the optical colorimetric sensor array based on optical probes(including organic molecular probes, polymer materials and nanomaterials). The research progress in the detection of metal ions, anions, toxic gases, organic compounds, biomolecules and living organisms(such as DNA, amino acids, proteins, microbes and cells) and actual sample mixtures are summarized here.The review illustrates the types, application advantages and development prospects of the optical colorimetric sensor array to help broad readers to understand the research progress in the application of chemical sensor array.
2017年
[2] Yuzhi Chen, Xiaomin Shi, Zhengliang Lu*, Xuefei Wang*, and Zhuo Wang*. A Fluorescent Probe for Hydrogen Peroxide in Vivo Based on the Modulation of Intramolecular Charge Transfer. Anal.Chem., 2017:acs.analchem.6b04810. (原文链接)
ABSTRACT
Endogenous hydrogen peroxide in vivo is related to many diseases, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. Although many probes for detection of H2O2 have been explored, rapid response probes are still expected for in vivo application. Here, a new probe (PAM-BN-PB) was designed based on an intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) process with three parts: phenanthroimidazole, benzonitrile, and phenyl boronate. By modulation ICT process of PAM-BN-PB, H2O2 in solution systems can be detected with good selectivity. The exogenous and endogenous H2O2 in normal living cells, ischemia-reperfusion injury cells, and animals all can be imaged by PAM-BN-PB.

[1] 苏姗, 马宇帆, 田立枚, 王卓. 四苯乙烯聚集诱导发光探针在生物成像和药物递送中的应用研究进展. 中国科学:化学, 2017(09):37-46.