Abstract
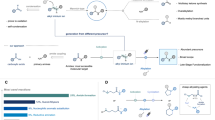
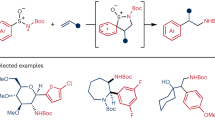
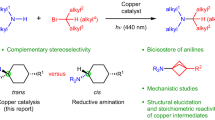
The ubiquity of tertiary alkylamines in pharmaceutical and agrochemical agents, natural products and small-molecule biological probes1,2 has stimulated efforts towards their streamlined synthesis3,4,5,6,7,8,9. Arguably the most robust method for the synthesis of tertiary alkylamines is carbonyl reductive amination3, which comprises two elementary steps: the condensation of a secondary alkylamine with an aliphatic aldehyde to form an all-alkyl-iminium ion, which is subsequently reduced by a hydride reagent. Direct strategies have been sought for a ‘higher order’ variant of this reaction via the coupling of an alkyl fragment with an alkyl-iminium ion that is generated in situ10,11,12,13,14. However, despite extensive efforts, the successful realization of a ‘carbonyl alkylative amination’ has not yet been achieved. Here we present a practical and general synthesis of tertiary alkylamines through the addition of alkyl radicals to all-alkyl-iminium ions. The process is facilitated by visible light and a silane reducing agent, which trigger a distinct radical initiation step to establish a chain process. This operationally straightforward, metal-free and modular transformation forms tertiary amines, without structural constraint, via the coupling of aldehydes and secondary amines with alkyl halides. The structural and functional diversity of these readily available precursors provides a versatile and flexible strategy for the streamlined synthesis of complex tertiary amines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Materials and methods, experimental procedures, useful information, mechanistic studies, optimization studies, 1H NMR spectra, 13C NMR spectra and mass spectrometry data are available in the Supplementary Information. Raw data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Roughley, S. D. & Jordan, A. M. The medicinal chemist’s toolbox: an analysis of reactions used in the pursuit of drug candidates. J. Med. Chem. 54, 3451–3479 (2011).
Blakemore, D. C. et al. Organic synthesis provides opportunities to transform drug discovery. Nat. Chem. 10, 383–394 (2018).
Abdel-Magid, A. F. & Mehrman, S. J. A review on the use of sodium triacetoxyborohydride in the reductive amination of ketones and aldehydes. Org. Process Res. Dev. 10, 971–1031 (2006).
Robak, M. T., Herbage, M. A. & Ellman, J. A. Synthesis and applications of tert-butanesulfinamide. Chem. Rev. 110, 3600–3740 (2010).
Huang, L., Arndt, M., Gooßen, K., Heydt, H. & Gooßen, L. J. Late transition metal-catalyzed hydroamination and hydroamidation. Chem. Rev. 115, 2596–2697 (2015).
Pirnot, M. T., Wang, Y.-M. & Buchwald, S. L. Copper hydride catalyzed hydroamination of alkenes and alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 48–57 (2016).
Musacchio, A. J. et al. Catalytic intermolecular hydroaminations of unactivated olefins with secondary alkyl amines. Science 355, 727–730 (2017).
Matier, C. D., Schwaben, J., Peters, J. C. & Fu, G. C. Copper-catalyzed alkylation of aliphatic amines induced by visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 17707–17710 (2017).
Grogan, G. Synthesis of chiral amines using redox biocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 43, 15–22 (2018).
Friestad, G. K. Addition of carbon-centered radicals to imines and related compounds. Tetrahedron 57, 5461–5496 (2001).
Reiber, H. G. & Stewart, T. D. The tetra alkyl methylene immonium salts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62, 3026–3030 (1940).
Paukstelis, J. W. & Cook, A. G. in Enamines: Synthesis, Structure and Reactions 2nd edn (ed. Cook, A. G.) Ch. 6, 275–346 (Marcel Dekker, 1988).
Bloch, R. Additions of organometallic reagents to C=N bonds: reactivity and selectivity. Chem. Rev. 98, 1407–1438 (1998).
Kaiser, E. M. Lithium: annual survey covering the year 1975. J. Organomet. Chem. 130, 1–131 (1977).
Werner, V., Ellwart, M., Wagner, A. J. & Knochel, P. Preparation of tertiary amines by the reaction of iminium ions derived from unsymmetrical aminals with zinc and magnesium organometallics. Org. Lett. 17, 2026–2029 (2015).
Saidi, M. R. & Nazari, M. Aminoalkylation with aldehydes mediated by solid lithium perchlorate. Monatsh. Chem. 135, 309–312 (2004).
Agosti, A., Britto, S. & Renaud, P. An efficient method to convert lactams and amides into 2,2-dialkylated amines. Org. Lett. 10, 1417–1420 (2008).
Haurena, C., LeGall, E., Sengmany, S. & Martens, T. Chiral amines in the diastereoselective Mannich-related multicomponent synthesis of diarylmethylamines, 1,2-diarylethylamines, and β-arylethylamines. Tetrahedron 66, 9902–9911 (2010).
Wu, P., Givskov, M. & Nielsen, T. E. Reactivity and synthetic applications of multicomponent Petasis reactions. Chem. Rev. 119, 11245–11290 (2019).
Aschwanden, P. & Carreira, E. M. in Acetylene Chemistry: Chemistry, Biology and Material Science (eds Diederich, F., Stang, P. J. & Tywinski, R. R.) (Wiley, 2005).
Lauder, K., Toscani, A., Scalacci, N. & Castagnolo, D. Synthesis and reactivity of propargylamines in organic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 117, 14091–14200 (2017).
Heinz, C. et al. Ni-catalyzed carbon–carbon bond-forming reductive amination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 2292–2300 (2018).
Chen, T.-Y., Tsutsumi, R., Montgomery, T. P., Volchkov, I. & Krische, M. J. Ruthenium-catalyzed C–C coupling of amino alcohols with dienes via transfer hydrogenation: redox-triggered imine addition and related hydroaminoalkylations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 1798–1801 (2015).
Miyabe, H., Yoshioka, E. & Kohtani, S. Progress in intermolecular carbon radical addition to imine derivatives. Curr. Org. Chem. 14, 1254–1264 (2010).
Friestad, G. K. Radical additions to chiral hydrazones: stereoselectivity and functional group compatibility. Top. Curr. Chem. 320, 61–91 (2011).
Tauber, J., Imbri, D. & Opatz, T. Radical addition to iminium ions and cationic heterocycles. Molecules 19, 16190–16222 (2014).
Russell, G. A., Yao, C.-F., Rajaratnam, R. & Kim, B. H. Promotion of electron transfer by protonation of nitrogen-centered free radicals. The addition of radicals to iminium ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 373–375 (1991).
Baguley, P. A. & Walton, J. C. Flight from the tyranny of tin: the quest for practical radical sources free from metal encumbrances. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37, 3072–3082 (1998).
Chatgilialoglu, C., Ferreri, C., Landais, Y. & Timokhin, V. I. Thirty years of (TMS) 3SiH: a milestone in radical-based synthetic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 118, 6516–6572 (2018).
Le, C., Chen, T. Q., Liang, T., Zhang, P. & MacMillan, D. W. C. A radical approach to the copper oxidative addition problem: trifluoromethylation of bromoarenes. Science 360, 1010–1014 (2018).
Cheng, Y., Mück-Lichtenfeld, C. & Studer, A. Metal-free radical borylation of alkyl and aryl iodides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 16832–16836 (2018).
Bahamonde, A. & Melchiorre, P. Mechanism of the stereoselective α-alkylation of aldehydes driven by the photochemical activity of enamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 8019–8030 (2016).
Fawcett, A. et al. Photoinduced decarboxylative borylation of carboxylic acids. Science 357, 283–286 (2017).
Lei, L. et al. Systematic study on alkyl iodide initiators in living radical polymerization with organic catalysts. Macromolecules 47, 6610–6618 (2014).
Bosma, R. et al. Route to prolonged residence time at the histamine H1 receptor: growing from desloratadine to rupatadine. J. Med. Chem. 62, 6630–6644 (2019).
Atzrodt, J., Derdau, V., Kerr, W. J. & Reid, M. Deuterium- and tritium-labelled compounds: applications in the life sciences. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 1758–1784 (2018).
Trowbridge, A., Reich, D. & Gaunt, M. J. Multicomponent synthesis of tertiary alkylamines by photocatalytic olefin-hydroaminoalkylation. Nature 561, 522–527 (2018).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Swiss National Science Foundation (R.K.), the Gates Cambridge Trust (N.J.F.), the EPSRC (W.G.W.) and the Royal Society (for a Wolfson Merit Award, M.J.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.K., N.J.F., W.G.W. and M.J.G. conceived the project; R.K., N.J.F. and W.G.W. conducted and analysed the experiments; and R.K., N.J.F., W.G.W. and M.J.G. wrote the manuscript. N.J.F. and W.G.W. contributed equally to the project and are listed alphabetically.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information 1
This file contains Materials and Methods, Supplementary Text, Supplementary Figures 1 to 9 and Supplementary Tables 1 to 2.
Supplementary Information 2
This file contains Supplementary Comparative Experimental Information, Supplementary Literature Overview and Supplementary Figures 1 to 3. information.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Flodén, N.J., Whitehurst, W.G. et al. A general carbonyl alkylative amination for tertiary amine synthesis. Nature 581, 415–420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2213-0