-
 RNA Sequencing and Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Highlight DNA Replication and Key Genes in Nucleolin-Depleted Hepatoblastoma Cells
RNA Sequencing and Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Highlight DNA Replication and Key Genes in Nucleolin-Depleted Hepatoblastoma Cells -
 An Updated Analysis of Exon-Skipping Applicability for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Using the UMD-DMD Database
An Updated Analysis of Exon-Skipping Applicability for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Using the UMD-DMD Database -
 Update on Inherited Pediatric Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Features and Outcome
Update on Inherited Pediatric Motor Neuron Diseases: Clinical Features and Outcome -
 Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics
Illumina SBS Sequencing and DNBSEQ Perform Similarly for Single-Cell Transcriptomics -
 Sleep Abnormalities in SLC13A5 Citrate Transporter Disorder
Sleep Abnormalities in SLC13A5 Citrate Transporter Disorder
Journal Description
Genes
Genes
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of genetics and genomics published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (SEBBM) is affiliated with Genes and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Genetics and Heredity) / CiteScore - Q2 (Genetics (clinical))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2023)
Latest Articles
Responses of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family to Drought Stress in Broomcorn Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.)
Genes 2025, 16(4), 368; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040368 (registering DOI) - 23 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.), a drought-tolerant C4 crop, is crucial for agricultural resilience in arid regions. Lipoxygenases (LOXs), key enzymes in plant stress responses, have not been studied in broomcorn millet. This study aimed to identify LOX genes in broomcorn
[...] Read more.
Background: Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.), a drought-tolerant C4 crop, is crucial for agricultural resilience in arid regions. Lipoxygenases (LOXs), key enzymes in plant stress responses, have not been studied in broomcorn millet. This study aimed to identify LOX genes in broomcorn millet and elucidate their role in drought tolerance. Methods: We employed bioinformatics and physiological analyses to identify LOX genes in broomcorn millet. Expression profiles were assessed in different organs, and drought stress responses were evaluated in tolerant (HSZ, YXDHM) and sensitive (YS10) varieties. Antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, POD, CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured. Results: Twelve LOX genes were identified, classified into three subfamilies, and mapped across seven chromosomes. These genes contained stress-responsive cis-elements and showed organ-specific expression, with PmLOX5 exhibiting no detectable expression. Under drought stress, tolerant varieties showed elevated antioxidant activities and reduced MDA accumulation. PmLOX2, a homolog of Arabidopsis AtLOX1/AtLOX5, was significantly induced in tolerant varieties, correlating with enhanced antioxidant capacity and reduced oxidative damage. Conclusions:PmLOX genes, particularly PmLOX2, play a pivotal role in drought tolerance by modulating ROS scavenging and membrane protection. This study provides a foundation for leveraging LOX genes to improve drought resilience in broomcorn millet and related crops.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioinformatics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Salt Tolerance and Transcriptomics in Two Varieties of Agropyron desertorum at Different Developmental Stages
by
Yuchen Li, Xintian Huang, Xiao Han, Hui Yang and Yan Zhao
Genes 2025, 16(4), 367; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040367 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Most of the grasslands in China are experiencing varying degrees of degradation, desertification, and salinization (collectively referred to as the “three degradations”), posing a serious threat to the country’s ecological security. Agropyron desertorum, known for its wide distribution, strong adaptability, and
[...] Read more.
Background: Most of the grasslands in China are experiencing varying degrees of degradation, desertification, and salinization (collectively referred to as the “three degradations”), posing a serious threat to the country’s ecological security. Agropyron desertorum, known for its wide distribution, strong adaptability, and resistance, is an excellent grass species for the ecological restoration of grasslands affected by the “three degradations”. This study focused on two currently popular varieties of A. desertorum, exploring their salt tolerance mechanisms and identifying candidate genes for salt and alkali tolerance. Methods: Transcriptome sequencing was performed on two varieties of A. desertorum during the seed germination and seedling stages under varying degrees of saline–alkali stress. At the seed stage, we measured the germination rate, relative germination rate, germination index, and salt injury rate under different NaCl concentrations. During the seedling stage, physiological indicators, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), malondialdehyde (MDA), proline (PRO), soluble protein (SP), and catalase (CAT), were analyzed after exposure to 30, 60, 120, and 180 mM NaCl for 12 days. Analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) at 6 and 24 h post-treatment with 120 mM NaCl revealed significant differences in the salt stress responses between the two cultivars. Results: Our study indicates that during the seed stage, A. desertorum (Schult.) exhibits a higher relative germination potential, relative germination rate, and relative germination index, along with a lower relative salt injury rate compared to A. desertorum cv. Nordan. Compared with A. desertorum cv. Nordan, A. desertorum (Schult.) has higher salt tolerance, which is related to its stronger antioxidant activity and different antioxidant-related pathways. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were used to identify the key biological processes and pathways involved in salt tolerance, including plant hormone signal transduction, antioxidant defense, and cell membrane stability. Conclusions: A. desertorum (Schult.) exhibits stronger salt tolerance than A. desertorum cv. Nordan. Salt stress at a concentration of 30–60 mM promotes the germination of the seeds of both Agropyron cultivars. The two Agropyron plants mainly overcome the damage caused by salt stress through the AsA-GSH pathway. This study provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms of salt tolerance in Agropyron species and lays the groundwork for future breeding programs aimed at improving salt tolerance in desert grasses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetics and Breeding of Forage)
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Mechanism of HINTW (HINT Gene in W-Chromosome)-Mediated UBE2I (Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme E2 I) Interaction in Female Differentiation of Chicken Embryos
by
Changhua Sun, Jiuzhou Song, Malik Ahsan Ali, Hongyan Sun, Yingjie Niu, Qisheng Zuo, Wei Han, Bichun Li and Kai Jin
Genes 2025, 16(4), 366; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040366 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: It has been established that HINTW plays a pivotal role in the female differentiation of chickens; nevertheless, the underlying molecular mechanism remains to be fully elucidated. Method: To investigate the role of HINTW in avian sex determination, a prokaryotic expression vector containing
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: It has been established that HINTW plays a pivotal role in the female differentiation of chickens; nevertheless, the underlying molecular mechanism remains to be fully elucidated. Method: To investigate the role of HINTW in avian sex determination, a prokaryotic expression vector containing its key structural domain was constructed, and its in vitro expression was achieved. Pull-down assays were performed to capture interacting proteins from male and female gonadal tissues, followed by a silver staining analysis to compare interaction profiles between ovaries and testes. Mass spectrometry was utilized to identify differentially bound proteins. Additionally, functional characterization and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays were conducted to validate the interaction between HINTW and its candidate binding partner. Result: A total of 1590 differentially bound proteins were identified between ovarian and testicular tissues. Functional analysis and Co-IP assays confirmed a specific interaction between HINTW and UBE2I in the ovary, suggesting that HINTW may facilitate female differentiation in chicken embryos through its interaction with UBE2I. Conclusions: This study provides novel insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying HINTW-mediated female differentiation in chickens and contributes to a deeper understanding of avian sex determination.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis of the Effects of Metformin on the Regeneration of Planarian Dugesia japonica
by
Zelong Zhao, Dandan Yin, Kexin Yang, Chunmei Zhang, Linxia Song and Zhenbiao Xu
Genes 2025, 16(4), 365; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040365 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Metformin is a widely used oral hypoglycemic agent for treating type 2 diabetes. Planarians, with their remarkable regenerative abilities, are frequently employed as model organisms in stem cell and regeneration studies. This study aimed to investigate the effects of metformin on planarian
[...] Read more.
Background: Metformin is a widely used oral hypoglycemic agent for treating type 2 diabetes. Planarians, with their remarkable regenerative abilities, are frequently employed as model organisms in stem cell and regeneration studies. This study aimed to investigate the effects of metformin on planarian regeneration, focusing on the regeneration of eyespots after amputation. Methods: Regenerating planarians with amputated eyespots were exposed to various concentrations of metformin. The regeneration time of the eyespots was measured to assess the effects of metformin. Subsequently, a 1 mmol/L metformin treatment for 24 h was applied to the planarians, followed by transcriptome analysis to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The gene expression was validated through qPCR. The full-length gene of casein kinase 1α (DjCK1α) was cloned using RACE technology. DjCK1α interference was performed to examine its role in regeneration. Results: Low concentrations of metformin significantly reduced the regeneration time of planarians. Transcriptome analysis identified 113 DEGs, including 61 upregulated and 52 downregulated genes. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses were conducted. Notably, DjCK1α, a key gene involved in regeneration, was selected for further validation. qPCR confirmed that DjCK1α was significantly upregulated. The interference of DjCK1α prolonged the regeneration time of the eyespots of planarians cultured in water, while treatment with metformin did not promote the eyespot regeneration of the DjCK1α-interfered planarians. Conclusions: The results suggest that metformin accelerates planarian eyespot regeneration, potentially through the regulation of DjCK1α. This study provides the first transcriptome-based analysis of drug effects on regeneration in planarians, highlighting the role of metformin in the regeneration process.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessReview
Evaluation of DNA in Human Teeth—Ante-Mortem and Post-Mortem Factors Affecting Degradation and Preservation: A Literature Review
by
Ana María Salazar, Patricia Alejandra Huerta, Viviana Coliboro-Dannich, Ariel F. Castro and Anna Barbaro
Genes 2025, 16(4), 364; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040364 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The identification of human remains is a major challenge in forensic science, particularly in cases of advanced decomposition. Human teeth are among the most resilient tissues to environmental and post-mortem degradation, making them a valuable source of DNA for forensic identification. However, DNA
[...] Read more.
The identification of human remains is a major challenge in forensic science, particularly in cases of advanced decomposition. Human teeth are among the most resilient tissues to environmental and post-mortem degradation, making them a valuable source of DNA for forensic identification. However, DNA preservation in teeth is influenced by multiple factors that can compromise the success of genetic analysis. Objective: This review analyzes the intrinsic and extrinsic factors affecting DNA preservation in human teeth, focusing on ante-mortem and post-mortem variables rather than the methodological aspects of DNA extraction and analysis. Methodology: A review of the literature was conducted, evaluating studies that assess the impact of biological factors (such as dental structure, pathology, and treatment) and environmental conditions (such as burial environment, temperature, and humidity) on DNA degradation in human teeth. Results: The findings indicate that DNA preservation is significantly influenced by the type of tooth, the presence of dental restorations or pathological conditions, and exposure to environmental factors. While some studies address these variables individually, forensic cases often involve complex interactions among multiple factors, making DNA recovery outcomes unpredictable. Conclusions: The degradation of DNA in human teeth results from a multifactorial process where intrinsic and extrinsic elements interact dynamically. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for optimizing sampling strategies and improving DNA recovery success rates in forensic applications. Future research should aim to develop predictive models that account for these variables, enabling more effective case-specific approaches to forensic DNA analysis.
Full article
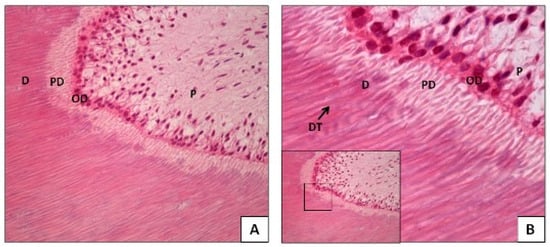
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Whole-Genome Resequencing in Sheep: Applications in Breeding, Evolution, and Conservation
by
Ruoshan Ma, Ying Lu, Mengfei Li, Zhendong Gao, Dongfang Li, Yuyang Gao, Weidong Deng and Bo Wang
Genes 2025, 16(4), 363; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040363 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
Sheep (Ovis aries) were domesticated around 10,000 years ago and have since become an integral part of human agriculture, providing essential resources, such as wool, meat, and milk. Over the past century, advances in communication and agricultural productivity have driven the
[...] Read more.
Sheep (Ovis aries) were domesticated around 10,000 years ago and have since become an integral part of human agriculture, providing essential resources, such as wool, meat, and milk. Over the past century, advances in communication and agricultural productivity have driven the evolution of selective breeding practices, further enhancing the value of sheep in the global economy. Recently, the rapid development of whole-genome resequencing (WGR) technologies has significantly accelerated research in sheep molecular biology, facilitating the discovery of genetic underpinnings for critical traits. This review offers a comprehensive overview of the evolution of whole-genome resequencing and its application to sheep genetics. It explores the domestication and genetic origins of sheep, examines the genetic structure and differentiation of various sheep populations, and discusses the use of WGR in the development of genetic maps. In particular, the review highlights how WGR technology has advanced our understanding of key traits, such as wool production, lactation, reproductive performance, disease resistance, and environmental adaptability. The review also covers the use of WGR technology in the conservation and sustainable utilization of sheep genetic resources, offering valuable insights for future breeding programs aimed at enhancing the genetic diversity and resilience of sheep populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
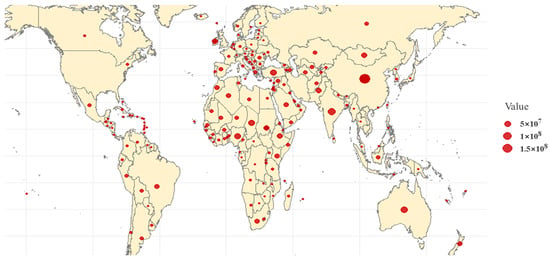
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Melatonin on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage of the Granulosa Cells in Hen Ovarian Follicles
by
Sheng Wang, Yu Ou, Shengxiao Cao, Xue Sun, Ning Qin, Simushi Liswaniso and Rifu Xu
Genes 2025, 16(4), 362; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040362 (registering DOI) - 22 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: The egg-laying performance of hens is primarily regulated by ovarian follicle growth and development; these follicles are susceptible to oxidative damage caused by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oxidative damage can lead to follicular atresia and impaired reproductive performance. Melatonin (MT), a
[...] Read more.
Background: The egg-laying performance of hens is primarily regulated by ovarian follicle growth and development; these follicles are susceptible to oxidative damage caused by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS). Oxidative damage can lead to follicular atresia and impaired reproductive performance. Melatonin (MT), a known endogenous antioxidant, plays a role in regulating oxidative damage, but its precise mechanisms in mitigating H2O2-induced oxidative damage via mitophagy regulation in granulosa cells remain unclear. Methods: An in vitro oxidative damage model was established by determining the optimal H2O2 concentration using CCK-8 fluorescence quantification. The optimal MT concentration was identified through fluorescence quantification and catalase (CAT) activity assays. The protective effects of MT against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in follicular granulosa cells were investigated using flow cytometry, Western blotting, ELISA, and quantitative fluorescence analysis. Results: An in vitro oxidative damage model was established using H2O2-induced granulosa cells, characterized by P53 and LC3-II upregulation and LC3-I and BCL-2 downregulation. The optimal MT concentration for reducing cellular injury was determined. MT co-treatment enhanced CAT, GSH, and SOD activities, decreased LC3-II/LC3-I conversion, and increased P62 expression. Furthermore, MT reduced autophagic vesicle formation and restored mitochondrial membrane potential, demonstrating its protective effect against H2O2-induced oxidative damage. Conclusions: Melatonin alleviates H2O2-induced oxidative damage in chicken follicular granulosa cells by modulating antioxidant defense, autophagy, and mitochondrial function. These findings provide newer insights to our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying the alleviation of the H2O2-induced oxidative damage in granulosa cells during ovarian follicle development in chickens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
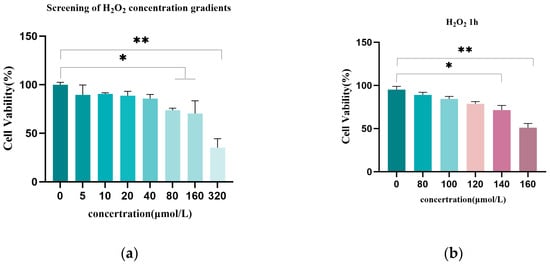
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic and Epigenetic Diversity of Pinus pinea L.: Conservation Implications for Priority Populations in Greece
by
Evangelia V. Avramidou, Ermioni Malliarou, Evangelia Korakaki, George Mantakas and Konstantinos Kaoukis
Genes 2025, 16(4), 361; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040361 (registering DOI) - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) is an evergreen coniferous species valued for its edible seeds, which provide significant economic benefits to local populations. Remarkable phenotypic plasticity but low genetic variation characterizes the species. In Greece, natural populations of P. pinea
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The stone pine (Pinus pinea L.) is an evergreen coniferous species valued for its edible seeds, which provide significant economic benefits to local populations. Remarkable phenotypic plasticity but low genetic variation characterizes the species. In Greece, natural populations of P. pinea are part of the Natura 2000 network and are protected under Annex I Priority Habitat type 2270. These populations, located across six Natura 2000 sites (including two islands), face increasing threats from tourism and climate change, leading to ecosystem degradation. Genetic and epigenetic studies are critical for the conservation of forest species because they provide insights into the genetic diversity, adaptive potential, and resilience of species, helping to inform effective management strategies and protect biodiversity in changing environments. This study aims to assess the genetic and epigenetic diversity of P. pinea in four Natura 2000 sites using molecular markers and to propose conservation strategies to ensure the species’ long-term sustainability. Additionally, a preliminary investigation of water potential under maximum daily water demand was conducted to evaluate the species’ adaptive response. Methods: Genetic analysis was performed using Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) markers, while epigenetic analysis was conducted using Methylation-Susceptible Amplified Polymorphism (MSAP) markers. Sampling was carried out in four Natura 2000 areas, where genetic and epigenetic diversity patterns were examined. Furthermore, a preliminary study on water potential under peak daily water demand conditions was conducted to assess the species’ physiological adaptation to environmental stress. Results: The results of this study provide valuable insights into conservation strategies by highlighting the potential role of epigenetic variation in the adaptability of P. pinea, despite its low genetic variability. Understanding the species’ epigenetic flexibility can inform conservation efforts aimed at enhancing its resilience to environmental stressors, such as climate change. Additionally, the preliminary water potential analysis contributes to identifying physiological traits that may help predict the species’ survival under varying environmental conditions, guiding the development of more targeted conservation practices and management plans. Further research could refine these findings and strengthen their application in conservation efforts. Conclusions: The conclusions emphasize the critical importance of this research in informing conservation efforts for P. pinea in Greece, particularly considering climate change and human pressures. The results highlight the need for both in-situ and ex-situ conservation strategies to ensure the long-term sustainability of the species. The key recommendations include the protection of natural habitats, the implementation of controlled seed collection practices, and further research into the epigenetic mechanisms that may enhance the species’ resilience to environmental stress. Future studies should focus on deepening our understanding of these epigenetic factors and their role in the adaptability of P. pinea, which will be essential for developing more effective conservation measures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessReview
Reproductive Choices in Haemoglobinopathies: The Role of Preimplantation Genetic Testing
by
Georgia Kakourou, Christina Vrettou, Thalia Mamas and Joanne Traeger-Synodinos
Genes 2025, 16(4), 360; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040360 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Haemoglobinopathies are among the most prevalent genetic disorders globally. In the context of these conditions, preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) plays a pivotal role in preventing genetic diseases in the offspring of carrier parents, reducing the need for pregnancy termination and enabling the selection
[...] Read more.
Haemoglobinopathies are among the most prevalent genetic disorders globally. In the context of these conditions, preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) plays a pivotal role in preventing genetic diseases in the offspring of carrier parents, reducing the need for pregnancy termination and enabling the selection of compatible sibling donors for potential stem cell transplantation in cases of thalassemia or sickle cell disease. This review explores the evolving role of PGT as a reproductive option for haemoglobinopathy carriers, tracing the development of PGT protocols from patient-specific to comprehensive testing enabled by advanced technologies like next-generation sequencing (NGS). We discuss key technical, biological, and practical limitations of PGT, as well as the ethical considerations specific to haemoglobinopathies, such as the complexity of interpreting genotypes. Emerging technologies, such as whole-genome sequencing, non-invasive PGT, and gene editing, hold significant promise for expanding applications but also raise new challenges that must be addressed. It will be interesting to explore how advancements in technology, along with the changing management of haemoglobinopathies, will impact reproductive choices. It is anticipated that continued research will improve genetic counseling for PGT for haemoglobinopathies, while a careful evaluation of ethical and societal implications is also required. Responsible and equitable implementation of PGT is essential for ensuring that all families at risk can make informed reproductive choices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances and Future Perspectives on Preimplantation Genetic Testing)
Open AccessArticle
Co-Expression Analysis of the ZDHHC19 Palmitoyltransferase–miR-4733–miR-596 Putative Regulatory Axis in Sepsis
by
Katalin Maricza, Zsuzsanna Elek, Eszter Losoncz, Krisztina Molnár, Zoltán Fülep, Réka Kovács-Nagy, Zsófia Bánlaki, Gergely Keszler and Zsolt Rónai
Genes 2025, 16(4), 359; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040359 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: ZDHHC19—a protein acyltransferase—is known to be induced in sepsis, a dysregulated immune response to infection, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. In this study, we aimed to explore whether upregulation of ZDHHC19 is modulated by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affecting
[...] Read more.
Background: ZDHHC19—a protein acyltransferase—is known to be induced in sepsis, a dysregulated immune response to infection, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain elusive. In this study, we aimed to explore whether upregulation of ZDHHC19 is modulated by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) affecting the binding of microRNA in the 3’ untranslated region of the gene. Methods: Inpatients with clinically verified severe infection (n = 83) or sepsis (n = 63) were recruited to the study. Genomic DNA and total RNA were prepared from buccal and peripheral blood samples, respectively. Genotyping of rs112579116 and rs2293161 SNPs was performed by TaqMan real-time PCR assays, while ZDHHC19 mRNA as well as miR-4733 and -596 microRNA levels were quantitated by reverse transcription qPCR. Correlations between genotypes, expression levels and clinical parameters were assessed by the Shapiro–Wilk, Mann–Whitney and t-tests. Results: Transcript levels of ZDHHC19 were significantly enhanced in septic blood samples (p = 0.0000709) and associated with clinical parameters such as procalcitonin levels, blood cell counts and clotting factors. Levels of both miRNAs showed an inverse but not significant correlation with those of ZDHHC19. Conclusions: Expression of ZDHHC19 should be considered a reliable molecular marker of sepsis, but further investigations are needed to shed light on regulatory mechanisms involved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessArticle
An Analysis of the Genetic Diversity, Genetic Structure, and Selection Signal of Beagle Dogs Using SNP Chips
by
Haolong Wang, Yanbo Yin, Can Zhang, Fangzheng Li, Haiping Zhao, Zhen Liu, Weili Sun and Lisheng Zhou
Genes 2025, 16(4), 358; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040358 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Beagle dogs are widely used in biomedical research, but their genetic diversity and population structure require further investigation. This study aimed to assess genetic diversity, population structure, and selection signals in a foundational Beagle breeding population using genome-wide SNP genotyping. Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Background: Beagle dogs are widely used in biomedical research, but their genetic diversity and population structure require further investigation. This study aimed to assess genetic diversity, population structure, and selection signals in a foundational Beagle breeding population using genome-wide SNP genotyping. Methods: A total of 459 Beagle dogs (108 males, 351 females) were genotyped using the Canine 50K SNP chip. After quality control, 456 individuals and 31,198 SNPs were retained. Genetic diversity indices, principal component analysis (PCA), identity-by-state (IBS) distance, a genomic relationship matrix (G-matrix), runs of homozygosity (ROH), and Tajima’s D selection scans were analyzed. Results: The average minor allele frequency was 0.224, observed heterozygosity was 0.303, and expected heterozygosity was 0.305. A total of 2990 ROH segments were detected, with a mean inbreeding coefficient of 0.031. Phylogenetic analysis classified 106 stud dogs into 13 lineages. Selection signal analysis identified TTN (muscle function) and DLA-DRA, DLA-DOA, DLA-DMA (immune regulation) under selection. Conclusions: The Beagle population exhibits high genetic diversity and low inbreeding. To maintain genetic stability and ensure the long-term conservation of genetic resources, structured breeding strategies should be implemented based on lineage classifications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
Open AccessArticle
Genotype-Phenotype Correlation Insights Through Molecular Modeling Analysis in a Patient with Loeys-Dietz Syndrome
by
Galateia Stathori, Eleni Koniari, Dimitrios Vlachakis, Eleni Papanikolaou, George P. Chrousos and Christos Yapijakis
Genes 2025, 16(4), 357; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040357 - 21 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Pathogenic variants within the gene encoding transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) are responsible for Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS), a heritable thoracic aortic disease sharing clinical features with Marfan syndrome, including craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities as well as aortic root aneurysms and dissections. In
[...] Read more.
Background: Pathogenic variants within the gene encoding transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) are responsible for Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS), a heritable thoracic aortic disease sharing clinical features with Marfan syndrome, including craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities as well as aortic root aneurysms and dissections. In contrast to Marfan syndrome patients, who rarely develop aneurysms or dissections beyond the aortic root, LDS patients frequently exhibit vessel aneurysms in locations other than the aortic root. Here, we report the case of a 61-year-old patient who initially presented with marfanoid characteristics and an aortic root aneurysm and was presumed to have Marfan syndrome two decades ago. Later, the patient developed an abdominal aorta aneurysm, necessitating endovascular repair and stent placement. That fact raised doubts regarding the initial diagnosis of Marfan syndrome, and we decided to investigate the genetic cause of the disorder. Methods: Genetic testing was performed using WES analysis and Sanger sequencing. Results: The genetic analysis detected a de novo heterozygous pathogenic variant c.896G>A in exon 5 of the TGFB2 gene, resulting in the amino acid substitution p. Arg299Gln that has devastating destabilizing structural effects on 3D folding of the protein, as demonstrated by the molecular modeling study we performed. This variant is pathogenic for LDS type 4, partially consistent with the patient’s clinical presentation. Conclusions: Our case emphasizes the significance of precise clinical assessment and genetic verification in patients exhibiting marfanoid characteristics. Furthermore, our findings contribute to the understanding of the diverse clinical spectrum associated with this specific pathogenic variant of TGFB2, underscoring the importance of detailed clinical assessment in expanding knowledge of genotype-phenotype correlations. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for tailored and appropriate management of individuals with heritable thoracic aortic diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Craniofacial Genetics)
►▼
Show Figures
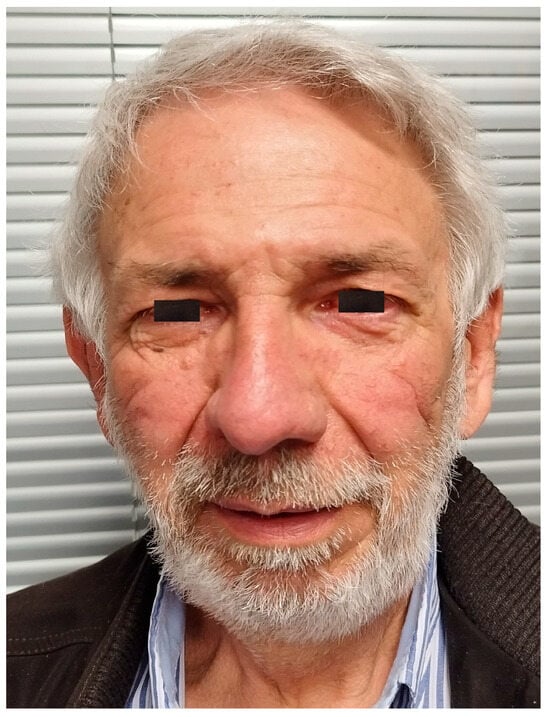

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum
by
Lorena Urbanelli, Federica Delo, Giada Cerrotti, Emidio Albertini, Jacopo Lucci, Sandra Buratta, Eleonora Calzoni, Stefano Giovagnoli, Luana Lugini, Cristina Federici, Federica Fratini, Valentino Mercati and Carla Emiliani
Genes 2025, 16(3), 356; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030356 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Plants release extracellularly lipid bilayer-enclosed vesicles of nanometric size that can be retrieved in their fluids. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) have mostly been involved in modulating host–pathogen interaction, making them a tool for cross-kingdom communication with a key role in plant immunity.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Plants release extracellularly lipid bilayer-enclosed vesicles of nanometric size that can be retrieved in their fluids. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) have mostly been involved in modulating host–pathogen interaction, making them a tool for cross-kingdom communication with a key role in plant immunity. In addition, PDEVs have demonstrated promising therapeutic features, not only in terms of intrinsic nutraceutical properties but also of active molecules’ delivery. Transgenic plants have been developed for a variety of purposes, i.e., to improve their functional properties like crops, but also to produce therapeutic molecules. However, it is unclear whether transgenes can end up in PDEVs, thus making them a vehicle for their cross-kingdom diffusion into the environment. Methods: Here, we investigated the association of transgenic DNA and RNA with PDEVs secreted by tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) engineered to express the neomycine phosphotransferase II (Npt-II) gene. PDEVs were isolated from leaf apoplastic fluid by ultracentrifugation and characterized for their morphology and size. The association of DNA and RNA was assessed by qRT-PCR and their immunomodulatory properties by assaying PDEVs-induced IL1β and IL10 on THP1 monocytes. Results: Npt-II RNA, but not DNA, could be amplified from PDEVs, whereas no differences were observed between wt and transgenic tobacco PDEVs in terms of immunomodulatory properties. Conclusions: Although a different behaviour by other types of RNAs or DNAs could still be possible, our findings indicate that in this model, PDEVs are not associated with transgenic DNA, but they can protect RNA, including transgenic RNA, from degradation, contributing to their cross-kingdom spreading.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
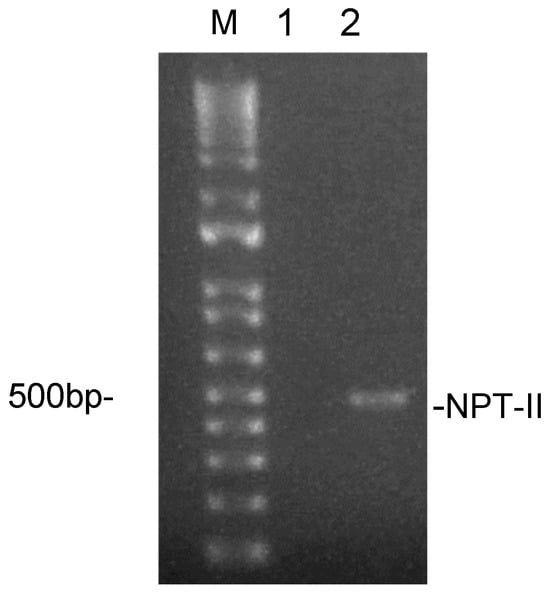
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The First Complete Mitochondrial Genomes for the Genus Dianema (Siluriformes: Callichthyidae): Dianema longibarbis and D. urostriatum
by
Seong Duk Do and Jae-Sung Rhee
Genes 2025, 16(3), 355; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030355 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: To date, no information is available on the complete mitochondrial genome of the genus Dianema (Siluriformes: Callichthyidae), a callichthyid catfish. In this study, we report on two complete mitochondrial genome sequences of Dianema longibarbis Cope, 1872, and Dianema urostriatum Miranda Ribeiro, 1912, the
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: To date, no information is available on the complete mitochondrial genome of the genus Dianema (Siluriformes: Callichthyidae), a callichthyid catfish. In this study, we report on two complete mitochondrial genome sequences of Dianema longibarbis Cope, 1872, and Dianema urostriatum Miranda Ribeiro, 1912, the only two recognized species within the genus Dianema. Methods: DNA sequencing was performed using the HiSeq platform to obtain their complete mitogenomes. To confirm phylogenetic distance, two phylogenetic trees were established using maximum-likelihood and Bayesian inference methods with all concatenated protein-coding sequences (PCGs) and two ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes from the D. longibarbis and D. urostriatum mitogenomes, along with 32 mitogenomes retrieved from Siluriformes. Results: The complete mitogenomes of D. longibarbis and D. urostriatum are 16,493 and 16,495 base pairs in length, respectively. Their nucleotide compositions are 31.79% A, 27.53% T, 25.86% C, and 14.82% G for D. longibarbis, and 31.69% A, 27.04% T, 26.36% C, and 14.91% G for D. urostriatum. Both mitogenomes contain 13 PCGs, 22 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes, and two rRNA genes. Phylogenetic results based on all PCGs and two rRNAs genes confirm D. longibarbis as a sister species to D. urostriatum in the subfamily Callichthyinae. Conclusions: In contrast to the extensive mitochondrial studies on species in the Corydoradinae, species in the Callichthyinae have been largely understudied. This study provides valuable insights into genetic diversity and evolutionary complexity by presenting the first mitochondrial genome analysis of two Dianema species, a genus within the Callichthyinae.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mitochondrial DNA Replication and Transcription)
►▼
Show Figures
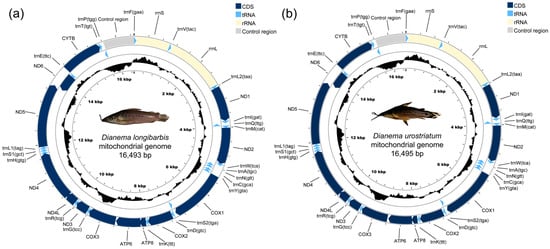
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Unique Case Report: A Rare Association of 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency with Triple X Karyotype
by
Rossana Santiago de Sousa Azulay, Alexandre Nogueira Facundo, Sarah Sousa e Sousa, Gilvan Cortes Nascimento, Marcelo Magalhães, Clariano Pires de Oliveira Neto, Joana D’arc Matos França de Abreu, Débora Cristina Ferreira Lago, Sabrina da Silva Pereira Damianse, Viviane Chaves de Carvalho, Caio Andrade Nascimento, Vandilson Pinheiro Rodrigues, Fernanda Borchers Coeli-Lacchini, Margaret de Castro and Manuel dos Santos Faria
Genes 2025, 16(3), 354; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030354 - 20 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) represents a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis in the adrenal glands. Over 90% of CAH cases result from a deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (21OHD). The clinical spectrum of 21OHD ranges from
[...] Read more.
Background: Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) represents a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis in the adrenal glands. Over 90% of CAH cases result from a deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (21OHD). The clinical spectrum of 21OHD ranges from the severe, life-threatening salt-wasting classic form, often presenting with prenatal virilization in females, to the non-classic (milder) form, which lacks glucocorticoid deficiency. Females with the non-classic form may experience symptoms of hyperandrogenism or infertility later in life, while males with non-classic CAH are often undiagnosed due to the subtler presentation. The coexistence of genetic anomalies and CAH is rarely reported in the literature, particularly in cases involving Triple X syndrome—a condition typically associated with a mild and frequently underdiagnosed clinical course. Case presentation: Here, we present a unique case of a 38-year-old woman with a history of premature ovarian failure and subsequent clinical features of hyperandrogenism. Further investigation revealed a novel association between partial 21OHD and a Triple X karyotype—an association not previously documented in the literature. Conclusions: This case highlights the potential for coexisting rare genetic conditions and underscores the critical importance of thorough and meticulous clinical evaluation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides from Nibribacter radioresistens, a UV and Gamma Radiation Tolerant Bacterium
by
Sam Woong Kim and Woo Young Bang
Genes 2025, 16(3), 353; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030353 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Nibribacter radioresistens, a UV and gamma radiation-tolerant bacterium, was reported to have superior antibacterial activities against a variety of pathogenic bacteria through the production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), but nothing is known about its AMPs. Methods/Results: In this study, our genomic
[...] Read more.
Background: Nibribacter radioresistens, a UV and gamma radiation-tolerant bacterium, was reported to have superior antibacterial activities against a variety of pathogenic bacteria through the production of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), but nothing is known about its AMPs. Methods/Results: In this study, our genomic and transcriptomic data showed that the N. radioresistens genome contains 11 AMP gene candidates, designated as NB_AMP1 to NB_AMP11, which are expressed differently in logarithmic growth and stationary phase. Moreover, the cell-free supernatant of all Escherichia coli DH5α strains containing cloned AMPs except for NB_AMP5 and NB_AMP7 exhibited antibacterial activities against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Synthetic AMPs supported the antibacterial activities of cloned AMPs, and, in particular, the synthetic NB_AMP2 showed superior antibacterial activities against both E. coli and S. aureus. Conclusions: Altogether, these results suggest that the AMP candidates from N. radioresistens may function as antimicrobial peptides, effectively causing cellular lysis through pore formation in the bacterial membrane.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbial Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Diversity and Forensic Parameters of 27 Y-STRs in Two Mestizo Populations from Western Mexico
by
Astrid Desireé Sánchez-Méndez, Silvia Elena Narvaez-Rivera, Héctor Rangel-Villalobos, Jorge Hernández-Bello, Andrés López-Quintero, José Miguel Moreno-Ortíz, Benito Ramos-González and José Alonso Aguilar-Velázquez
Genes 2025, 16(3), 352; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030352 - 19 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: Analyzing Y-chromosome short tandem repeats (Y-STRs) is essential in forensic genetics and population studies. The Yfiler™ Plus kit, which includes 27 Y-STR markers, enhances the discrimination power for forensic and kinship applications. However, this genetic system has not been analyzed in Mexican
[...] Read more.
Background: Analyzing Y-chromosome short tandem repeats (Y-STRs) is essential in forensic genetics and population studies. The Yfiler™ Plus kit, which includes 27 Y-STR markers, enhances the discrimination power for forensic and kinship applications. However, this genetic system has not been analyzed in Mexican populations, which limits its application and representativeness in international databases. Objectives: We wished to examine the genetic diversity and forensic parameters of the 27 Y-STRs included in the YFiler™ Plus kit in two populations from Western Mexico (Jalisco and Michoacán). Methods: Male DNA samples were amplified using the Yfiler™ Plus kit, followed by a fragment analysis via capillary electrophoresis (CE). The haplotype frequencies and forensic parameters were calculated. The haplogroups of all samples were predicted, and the distribution and percentages of ancestries were determined. The Rst genetic distances, including reference populations, were calculated and graphically represented in a multidimensional scaling (MDS) plot. Results: A total of 224 haplotypes were identified in all of the samples, of which 98.66% corresponded to unique haplotypes. Bi- and tri-allelic patterns were observed in both populations. The observed discriminatory capacity was 98.4% for Jalisco and 98.9% for Michoacán, while the haplotype diversity values were 0.9998 and 0.9997, respectively. The most frequent haplogroup was R1b, followed by Q, representing the European and Native American ancestries, in both populations. Conclusions: This study is the first to report the haplotype diversity and forensic parameters of the 27 Y-STRs included in the Yfiler™ Plus kit in Mexican populations. These findings confirm the forensic utility of these markers for human identification, biological relationship testing, and criminal investigations, reinforcing their applicability in forensic casework.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Genetic Diversification of Human Populations)
►▼
Show Figures
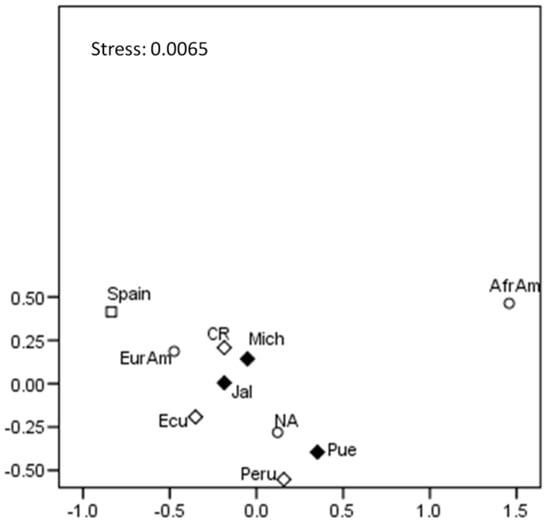
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SARS-CoV-2 Genetic Variants Identified in Selected Regions of Ethiopia Through Whole Genome Sequencing: Insights from the Fifth Wave of COVID-19
by
Getnet Hailu, Mengistu Legesse, Andargachew Mulu, Girmay Medhin, Mesfin Mengesha Tsegaye, Dawit Hailu Alemayehu, Abaysew Ayele, Atsbeha Gebreegziabxier, Adamu Tayachew, Adimkewu Aguine, Haileyesus Dejene, Sofonias K. Tessema, Harris Onywera, Assohoun Egomli Stanislas, Ebba Abate, Alessandro Marcello and Molalegne Bitew
Genes 2025, 16(3), 351; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030351 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted SARS-CoV-2 variants with increased transmissibility and immune evasion. In Ethiopia, where cases surged, the understanding of the virus’s dynamics was limited. This study analyzed SARS-CoV-2 variants during the fifth wave, crucial for guiding vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics, and understanding
[...] Read more.
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted SARS-CoV-2 variants with increased transmissibility and immune evasion. In Ethiopia, where cases surged, the understanding of the virus’s dynamics was limited. This study analyzed SARS-CoV-2 variants during the fifth wave, crucial for guiding vaccines, therapeutics, diagnostics, and understanding disease severity. Method: From June to August 2022, 150 SARS-CoV-2-positive samples were randomly selected from the Ethiopian Public Health Institute repository. Sixty-three high-quality genome sequences were analyzed. Results: Of the 63 sequences, 70% were from males and 30% from females, with a median age of 34. Omicron dominated (97%, 61/63), primarily clade 22A (64%, 40/63), followed by 22B (18%, 11/63) and 21K (14%, 9/63). Delta accounted for 3.2% (2/63). Omicron was identified in all (25) vaccinated study participants. Ethiopian sequences showed limited evolutionary divergence and lower genetic diversity compared to global sequences. Conclusion: Omicron was the predominant variant during Ethiopia’s fifth wave, indicating recent community transmission. Despite minor genetic diversity differences, ongoing surveillance remains critical for tracking variants and informing public health interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Alternative Splicing Events and ABA Hormone Regulation in Drought Response of Hippophae gyantsensis L.
by
Fanfan Lin, Yifan Cai, Shihai Yang and Yunqiang Yang
Genes 2025, 16(3), 350; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030350 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: Hippophae gyantsensis, a drought-tolerant plant native to the Tibetan Plateau, plays a crucial ecological and economic role. While its drought tolerance mechanisms have been extensively studied, the role of alternative splicing (AS) in drought resistance remains insufficiently explored. This
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Hippophae gyantsensis, a drought-tolerant plant native to the Tibetan Plateau, plays a crucial ecological and economic role. While its drought tolerance mechanisms have been extensively studied, the role of alternative splicing (AS) in drought resistance remains insufficiently explored. This study aims to elucidate how AS events regulate gene expression to enhance drought tolerance in H. gyantsensis under water-deficit conditions. (2) Methods: H. gyantsensis plants were subjected to progressive drought stress followed by rehydration. Physiological responses, transcriptomic data, and hormonal profiles were analyzed to investigate the plant’s adaptive mechanisms to drought stress, with a particular focus on abscisic acid (ABA) signaling-related genes. (3) Results: The results showed that H. gyantsensis maintained high leaf water content even under severe drought stress, emphasizing its strong drought resistance. A transcriptomic analysis revealed 11,962 differentially expressed genes, primarily enriched in hormone signaling and metabolic pathways. Notably, the accumulation of ABA was closely associated with AS events in ABA-related genes, such as ZEPs, ABCG, and PP2C. These genes produced multiple splice variants, indicating their role in modulating the ABA signaling pathway and enhancing drought tolerance. (4) Conclusions: This study highlights the pivotal role of AS in ABA signaling and drought tolerance in H. gyantsensis. It provides new insights into how AS contributes to plant adaptation to drought stress, bridging the knowledge gap in drought resistance mechanisms and emphasizing the importance of AS in plant stress responses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genes & Environments)
►▼
Show Figures
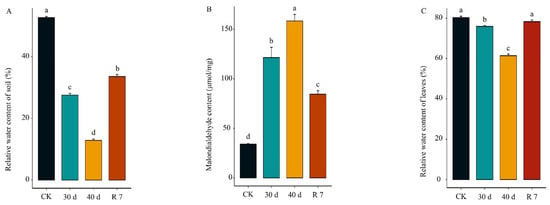
Figure 1

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Narrative Review
by
Francisca Villagrán-Silva, Pía Loren, Cristian Sandoval, Fernando Lanas and Luis A. Salazar
Genes 2025, 16(3), 349; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030349 - 17 Mar 2025
Abstract
In an obesogenic environment, such as the one we have been experiencing in recent decades, epigenetics provides answers to the relationship between hereditary and environmentally acquired patterns that have significantly contributed to the global rise in obesity prevalence. MicroRNA (miRNA) constitutes a diminutive
[...] Read more.
In an obesogenic environment, such as the one we have been experiencing in recent decades, epigenetics provides answers to the relationship between hereditary and environmentally acquired patterns that have significantly contributed to the global rise in obesity prevalence. MicroRNA (miRNA) constitutes a diminutive non-coding small RNA molecule, 20 to 24 nucleotides in length, that functions as a regulator of gene regulation at the post-translational level. Circulating miRNAs (c-miRNAs) have been detected in multiple body fluids, including blood, plasma, serum, saliva, milk from breastfeeding mothers, and urine. These molecules hold significant therapeutic value and serve as extracellular biomarkers in metabolic diseases. They aid in the diagnosis and tracking of therapy responses, as well as dietary and physical habit modifications. Researchers have studied c-miRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosing and characterizing systemic diseases in people of all ages and backgrounds since then. These conditions encompass dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular risk, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, and obesity. This review therefore analyzes the usefulness of c-miRNAs as therapeutic markers over the past decades. It also provides an update on c-miRNAs associated with general obesity and overweight, as well as with the most prevalent pathologies in the adult population. It also examines the effect of different nutritional approaches and physical activity regarding the activity of miRNAs in circulation in adults with overweight or general obesity. All of this is done with the aim of evaluating their potential use as biomarkers in various research contexts related to overweight and obesity in adults.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Ins and Outs of miRNAs as Biomarkers, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
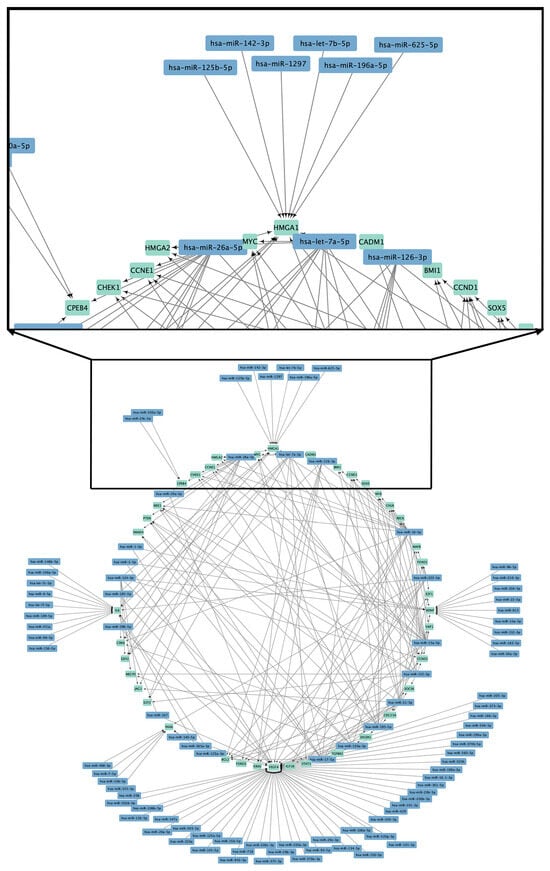
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Genes Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Biomolecules, Cells, JCM, Osteology, Genes, IJMS
Bone-Related Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapy Development
Topic Editors: Xiao Wang, Xin DongDeadline: 31 March 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cells, Genes, ncRNA, IJMS
MicroRNA: Mechanisms of Action, Physio-Pathological Implications, and Disease Biomarkers, 3rd Edition
Topic Editors: Hsiuying Wang, Y-h. TaguchiDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topic in
Diversity, Forests, Genes, IJPB, Plants
Plant Chloroplast Genome and Evolution
Topic Editors: Chao Shi, Lassaâd Belbahri, Shuo WangDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, BioMedInformatics, BioTech, Genes, Computation
Computational Intelligence and Bioinformatics (CIB)
Topic Editors: Marco Mesiti, Giorgio Valentini, Elena Casiraghi, Tiffany J. CallahanDeadline: 30 September 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Genes
Functional Genomics and Breeding of Animals
Guest Editor: Tingxian DengDeadline: 25 March 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Molecular Evolution, Mitochondrial Genomics and Mitochondrial Genome Expression in Animals: 2024–2025
Guest Editors: Jiayong Zhang, Jiasheng HaoDeadline: 25 March 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Developmental Biology and Genetics in Chicken Embryo Germ Cell
Guest Editors: Kai Jin, Yingjie NiuDeadline: 25 March 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Epigenetics in Human Development and Diseases
Guest Editors: Naila Francis Paulo De Oliveira, Maria Cristina Leme Godoy dos SantosDeadline: 25 March 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Genes
Genetics and Genomics of Hereditary Disorders of Connective Tissue
Collection Editors: Nazli B. Mcdonnell, Bert Callewaert, Clair A. Francomano, Philippe Khau-Van-Kien, Yves Dulac
Topical Collection in
Genes
Genotype-Phenotype Study in Disease
Collection Editors: Michele Cioffi, Maria Teresa Vietri
Topical Collection in
Genes
Genetics and Genomics of Rare Disorders
Collection Editors: Stefania Zampatti, Emiliano Giardina






